
The nature of word stress. The principles of word stress. The placement of word stress. Degrees of word stress.
By Eveline Podshivalova

The nature of word stress. The principles of word stress. The placement of word stress. Degrees of word stress.
Plan
- The nature of word stress.
- The principles of word stress.
- The placement of word stress.
- Degrees of word stress.

1. The nature of word stress.

Stress is a greater degree of prominence of a syllable or syllables as compared to the other syllables of the word.

The effect of prominence of the stressed syllable is achieved by a number of phonetic parameters such as :
- pitch;
- loudness;
- length;
- vowel quality.
As a result there appears a contrast between stressed and unstressed syllables.
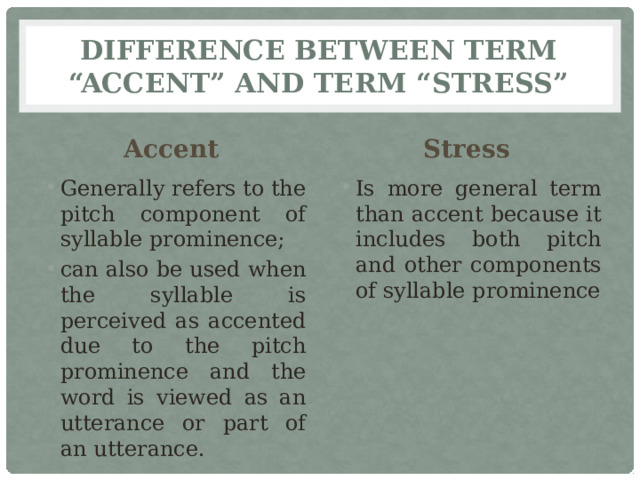
Difference between term “accent” and term “stress”
Accent
Stress
- Generally refers to the pitch component of syllable prominence;
- can also be used when the syllable is perceived as accented due to the pitch prominence and the word is viewed as an utterance or part of an utterance.
- Is more general term than accent because it includes both pitch and other components of syllable prominence
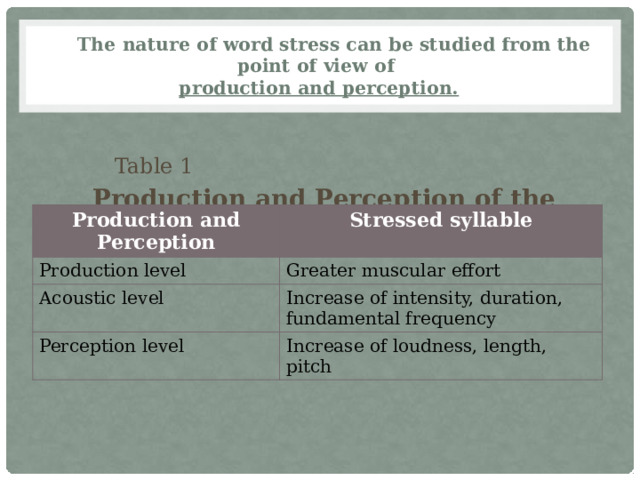
The nature of word stress can be studied from the point of view of production and perception.
Table 1
Production and Perception of the Stressed Syllables
Production and Perception
Production level
Stressed syllable
Acoustic level
Greater muscular effort
Increase of intensity, duration, fundamental frequency
Perception level
Increase of loudness, length, pitch

2. The principles of word stress.
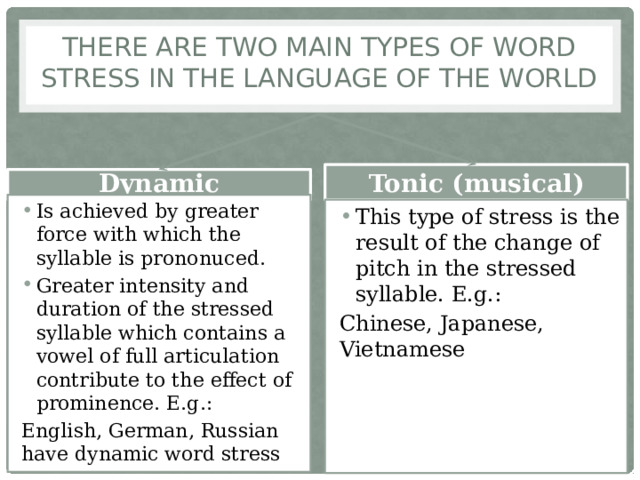
There are two main types of word stress in the language of the world
Tonic (musical)
Dynamic
- Is achieved by greater force with which the syllable is prononuced.
- Greater intensity and duration of the stressed syllable which contains a vowel of full articulation contribute to the effect of prominence. E.g.:
English, German, Russian have dynamic word stress
- This type of stress is the result of the change of pitch in the stressed syllable. E.g.:
Chinese, Japanese, Vietnamese

3. The placement of word stress.

According to its placement in a word stress can be fixed and free
- In languages with a fixed stress the position of the word stress is restricted to a particular syllable in a multisyllabic word.
In French word stress is normally fixed on the last syllable of the word.
- In languages with a free stress its location is not confined to a specific position in the word. In one word it may fall on the first syllable, in another on the second syllable, in the third word – on the last syllable and so on.
The number of languages with free word stress is relatively small: English, Russia, Italian, Greek…

In English (as well as in Russian) the word stress is not only free, but it also shifting , which means that it can change its position in different forms of the word and its derivatives:
- ‘ contrast - con’trast;
- ‘ music – mu’sician;
- ‘ habit – ha’bitual.

To define the position of word stress in an individual word it is helpful to consider the following factors:
- Phonological structure of the syllables or syllable weight is related to the status of a particular syllable in terms of the degree of sonority.
- The number of syllables in a word influences the number of stresses and to a certain extent the position of stress.
- The morphological factor , in particular, whether the word is simple, complex or compound. In complex the placement of stress depends on the type of suffix.
- Grammatical category the word belongs to.
‘ insult - in’sult, record – re’cord, ‘present – pre’sent

Suffixes are divided into:
1. Stress-neutral do not affect the stress placement in the stem: -al, -able, -en, -ful, -ing, -ish, -less, -ness, -ly, -ment,
-ous
re’fuse - re’fusal, ‘comfort – ‘comfortable, a’maze – a’mazing
2. Stress-fixing suffixes determine the placement of stress on a particular syllable of the stem: suffixes –ion, -ic, -ity, -ial, -ive attract stress to the syllable that precedes them
‘ perfect – per’fection, ‘proverb – pro’verbial
3. Stress attracting carry stress themselves: -ade, -eer, -ee,
- esque, -ette
- cru’sade, mounta’neer, refu’gee, ciga’rette, pictu’resque

4. Degrees of word stress.

The syllables in a word have different degrees of prominence. In English they generally distinguish three linguistically relevant degrees of stress:
- Primary (strong, main, principal).
- Secondary (half-strong, half-stressed).
- Weak (unstressed).

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











 Word stress in English (113.32 KB)
Word stress in English (113.32 KB)
 0
0 908
908 8
8 Нравится
0
Нравится
0





