ГАПОУ СПО «Казанский авиационно - технический колледж имени П.В.Дементьева»
READING FOR INFORMATION AND LEARNING
МЕТОДИЧЕСКОЕ УЧЕБНОЕ ПОСОБИЕ ПО АНГЛИЙСКОМУ ЯЗЫКУ ИНТЕГРИРОВАННОЕ С ДИСЦИПЛИНОЙ ГИДРАВЛИКА
(для студентов специальностей 24.02.01, 24.02.02, 15.02.08 КАТК им.П.В.Демнтьева)
Казань 2015
Авторы:
Татлыева Альфия Харисовна, Данилова Валентина Петровна
Рецензент:
Преподаватель высшей квалификационной категории Казанского педагогического колледжа Хуснутдинова Халида Асхатовна
«Reading for information and learning»: методическое учебное пособие по английскому языку для студентов специальностей 24.02.01, 24.02.02, 15.02.08 в Казанском авиационно- техническом колледже имени П.В.Дементьева/ А.Х.Татлыева,- типография КАТК им.П.В.Дементьева , 2015.- 22стр.
Методическое учебное пособие по английскому языку «Reading for information and learning» разработано для студентов 2 курсов, обучающихся по специальностям 24.02.01, 24.02.02, 15.02.08 в Казанском авиационно- техническом колледже имени П.В.Дементьева, интегрированное с дисциплиной гидравлика. Методическое пособие состоит из введения и двух разделов, включает в себя 8 аутентичных текстов.
Целью создания данного учебного пособия является научить студентов извлекать необходимую информацию по специальности из тематических (по гидравлике) текстов на английском языке. Для достижения данной цели разработана система упражнений. Материалы данного пособия помогают формировать навыки ознакомительного чтения с извлечением необходимой информации из профессиональных текстов.
Для создания учебного пособия использованы интернет ресурсы и основной учебник по гидравлике: А.В.Лепёшкин, А.А.Михайлин. Гидравлические и пневматические системы: учебник для среднего профессионального образования, -М.; Издательский центр «Академия», 2004.-336с.
Учебное пособие может быть использовано как на уроках английского языка, так и при самостоятельной работе студентов по дисциплине Английский язык.
Рецензия
на методическое учебное пособие по английскому языку «Reading for information and learning», для студентов специальностей 24.02.01, 24.02.02, 15.02.08 в Казанском авиационно- техническом колледже имени П.В.Дементьева, интегрированное с дисциплиной гидравлика, созданного преподавателем английского языка КАТК имени П.В.Дементьева, Татлыевой А.Х.
Данное учебное пособие составлено в качестве дополнительного учебника, содержащего аутентичные тексты по гидравлике на английском языке. Это учебное пособие способствует закреплению и углублению теоретических знаний по спец.дисциплине посредством английского языка. Так же способствует обучению извлечения необходимой информации из тематических технических текстов.
Учебное пособие представляет собой сборник аутентичных текстов и упражнений на закрепление тем. Каждый текст сопровождается глоссарием, что облегчает студентам работу с текстами. Так же имеются таблицы и схемы.
В данном учебном пособии отображена междисциплинарная связь с предметом гидравлика.
Учебное пособие по английскому языку «Reading for information and learning» может быть рекомендовано для использования как на занятиях английского языка, так и при самостоятельной работе студентов в данном учебном заведении.
Рецензент: преподаватель высшей квалификационной категории Казанского педагогического колледжа Х.А.Хуснутдинова
Content
Introduction. A brief overview of the development of mechanics of liquid bodies………………………………………………………………………………4
(Введение. Краткий обзор развития механики жидких тел)
The concept of the hydraulic drive……………………………………..….……….6
(Понятие гидропривода)
Topic 1.1. Working fluid and an oil.
1.1.1Appointment of the working fluid. Determination of liquid………….....……7
(Тема 1.1. Рабочие тела и масла.
1.1.1Назначение рабочей жидкости. Определение жидкости)
1.3.1 Types of fluid motion. Hydraulic fluid flow elements…….…………………8
(1.3.1Виды движения жидкости. Гидравлические элементы потока жидкости)
Topic 2.1. The structure and components of hydraulic drive.
2.1.1General information on hydraulic drives…………………………………….11
(Тема 2.1. Структура и составные элементы гидропривода.
2.1.1. Общие сведения о гидроприводах)
2.2.1 Function and classification of hydraulic machines. Main parameters……....13
(2.2.1.Назначение, классификация гидромашин. Основные параметры)
2.3.1. Purpose of devices. Classification. Main parameters………………........…15
(2.3.1. Назначение аппаратов. Классификация. Основные параметры)
2.6.1. Conformation and operation of the piston compressor………….………....18
(2.6.1.Устройство и принцип действия поршневого компрессора)
.
Introduction
A brief overview of the development of mechanics of liquid bodies.
1.Before reading the text, read the words and phrases from the text.
1. Treatise- трактат
2. Floating bodies- плавающие тела
3. Water pipeline- водопровод
4. Hydraulic structures-гидротехнические сооружения
5. Revival – возрождение
6. Picking up –собирание
7. Resistance of the liquid medium- сопротивление жидкой среды
8. Located inside area- расположенная внутри площадка
9. Square law- квадратичный закон
10. Friction- трение
11. Equilibrium- равновесие
12. Cover the period – охватывать период
13. Full (зд)- действительный
14. Reasoning - рассуждения
15. Body –тело
16. Universal natural law- всеобщий естественный закон
17. Matter- материя
18. Remarkable- замечательный
19. Applied issues- прикладные вопросы
2.Read the text and translate it into Russian
A. brief overview of the development of mechanics of liquid bodies.
Hydraulics is one of the oldest sciences, has evolved over twenty-two centuries. The first work in this field of knowledge was a treatise of ancient Greek geometry and mechanics of Archimedes (287-212. BC) "On Floating Bodies." At this stage it was built for water pipelines and hydraulic structures in the ancient states.
The next stage - the revival of hydraulics and picking up the individual elements in hydraulics - covers a period of three centuries (XV-XVIII centuries.).
To this period belong the works of Leonardo da Vinci on the resistance of the liquid medium moving in her body, the works of Galileo Galley on the basic laws of swimming bodies, Blaise Pascal about the independence of the pressure force of the fluid on the location inside the area, the works of Isaac Newton's square law of resistance fluid moving in her the body and on the law of friction liquid bodies.
Phase formation hydraulics as an independent science of motion and equilibrium liquid covers the period of the XVIII - XIX centuries.
The founders of the hydraulics were full members of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Mikhail Lomonosov, Leonhard Euler and Daniel Bernoulli. Mikhail Lomonosov, in his "Reasoning on the hardness and liquid bodies" for the first time brought a universal natural law of conservation of matter and energy, carried out a number of remarkable works of applied issues of fluid mechanics. L. Euler was the founder of the mathematical method of hydraulic - "classical fluid mechanics", based on the model of the "ideal" (without internal friction) liquid. Bernoulli was the founder of the method applied hydraulics - "hydraulic engineering" based on their deduced theorem, which establishes a relationship between height, pressure and fluid velocity.
The current stage of development of hydraulics covers the period of the XIX century, and is characterized by the synthesis methods of the "classical fluid mechanics" and the method of application "hydraulic engineering".
3.Answer to the question on the text
1.What is hydraulic? 2.What famous scientists were the founders of hydraulic?
4.Translate these sentences into English
1.Гидравлика является одной из древнейших наук. 2. М. В. Ломоносов в своей работе «Рассуждения о твердости и жидкости тел» впервые вывел всеобщий естественный закон сохранения материи и энергии. 3. На этом этапе были построены водопроводные и гидротехнические сооружения. 4. Современный этап развития характеризуется синтезом методов «классической гидромеханики» и метода прикладной «инженерной гидравлики»
5..Match the information in the table and write down sentences
| Names of scientists | Their works |
| 1) Galileo Galilei | a) was the founder of the method applied hyd- raulics- «hydraulic engineering» based on the theorem, which established a relationship between height, pressure, an fluid velocity. |
| 2) M.Lomonosov | b) was the first scientist who wrote treatise «About floating bodies» for building ancient water pipelines and hydraulic structures. |
| 3) Archimedes | c)wrote the works about the basic laws of swimming bodies |
| 4) L.Euler | d) brought a universal natural law of conservation of matter and energy in his work «argument about hardness and liquid bodies». |
| 5) D.Bernoulli | e) was the founder of the mathematical method of hydraulic «classical fluid mechanics», based on the model of the ideal liquid. |
|
|
|
The concept of the hydraulic drive.
1.Before reading the text, read the words and phrases from the text.
1. Drive- привод
2. Set of- набор, совокупность
3. Power source- источник энергии
4. Electric drive- электропривод
5. Pneumatic drive- пневмопривод
6. Pressurized fluid- жидкость под давлением
7. Embed- внедрять
8. Definding - определяющий
9. Volumetric- объемный
10. Working body- рабочий орган
11. Pumps with drive motors- насосы с приводящими двигателями
12. Accumulator tank- гидроемкость
2.Read the text and translate it into Russian
The concept of the hydraulic drive.
Drive is the set of mechanisms for transmitting motion from the power source to the element. Electric drive uses electrical energy. Pneumatic drive uses the energy of compressed air. Hydraulic drive uses the energy of the pressurized fluid.
The idea of using hydraulic drives for bulk power transmission occurred some time ago, but only with the years 1920 -1930 they began to actively embed in engineering. The main definding of hydraulic drive unit is its volumetric hydraulic motor, which goes out unit either directly or through a mechanical transmission connected to the working body of the mechanism. Besides the volumetric hydraulic motor, the hydraulic drive unit may include the following: pumps with drive motors, hydroapparts, air conditioning working fluid, accumulator tanks and hydraulic lines. Each of the device of the hydraulic drive performs certain functions.
3.Translate these sentences into English\
1.Электропривод использует электрическую энергию. 2. Идея использования объемных гидроприводов для передачи мощности возникла сравнительно недавно. 3. В состав гидропривода входят: насосы с приводящими двигателями, гидр аппараты, кондиционеры рабочих жидкостей, гидроемкости и гидролинии.
Topic 1.1. Working fluid and an oil.
1.1.1. Appointment of the working fluid. Determination of liquid.
1.Before reading the text, read the words and phrases from the text.
1. Flaw ability – текучесть
2. Variability- изменяемость
3. Primarily- прежде всего
4. A lubricating medium- смазываемая среда
5. Hydraulic machines – детали гидромашин
6. Coolant- теплоноситель
7. Washing medium- промывочная среда
8. Products of wear and dirt- продукт изнашивания и загрязнения
2.Read the text and translate it into Russian
Appointment of the working fluid. Determination of liquid.
Under liquid realize physical body having unlike solid flow ability and unlike gas very low variability of its volume (changing the pressure or temperature).
The working fluid used in the hydraulic drive, is primarily a source of energy, or the working fluid, ie, It provides transmission of mechanical energy from the pump to the hydraulic motor.
In addition, the working fluid performs the following functions:
• a lubricating medium. It provides lubrication of rubbing surfaces of parts of hydraulic machines;
• is the coolant. It transfers heat from the heated parts of the cold;
• a washing medium. When driving, it carries with it the products of wear and dirt;
• a means of conservation. It protects the surface of the parts hydraulic equipment from corrosion;
Since the operating mechanism in the hydraulic systems is a liquid, selecting a working fluid, operation and maintenance of hydraulic systems, it is necessary to know the physical properties of liquids.
3.Answer to the question on the text
1.What is liquid? 2. What is the function of working fluid in the hydraulic drive?
4.Translate these sentences into English.
1.Рабочая жидкость является энергоносителем. 2. Рабочая жидкость выполняет функцию смазывающей среды. 3. При движении рабочая жидкость уносит с собой продукты изнашивания и прочие загрязнения. 4. Рабочая жидкость осуществляет смазку трущихся поверхностей деталей гидромашин.
5..Match the translation in the table and write down sentences
| English | Russian |
| 1) The working fluid performs the function of a washing medium
| a) Рабочая жидкость выполняет функцию смазывающей среды |
| 2) The working fluid performs the function of is the coolant. | b) Рабочая жидкость является промывочной средой |
| 3) The working fluid performs the function of the working medium | c) Рабочая жидкость является средством консервации |
| 4) The working fluid performs the function of a lubricating medium | d) Рабочая жидкость является теплоносителем |
| 5) The working fluid performs the function of a means of conservation | e) Рабочая жидкость является рабочим телом |
|
|
|
1.3.1. Types of fluid motion. Hydraulic fluid flow elements.
1.Before reading the text, read the words and phrases from it.
1. Duct- канал
2. Porous bodies - пористые тела
3. Fluid flow around bodies- обтекание тела жидкостью
4. Distinctive – отличительный
5. Particle- частица
6. Resting- покоящийся
7. Viscosity- вязкость
8. To establish- устанавливать
9. Drain- вытекание
10. Tank- резервуар
11. Constant-постоянный
12. Jet (зд)- струя
13. Steady- устойчивый
14. Gravity-flow- безнапорный
15. Pressure- (зд) - напорный
16. Stream (зд) - струйка
17. The curve- кривая
18. Line current- линия тока
19. Closed loop- замкнутый контур
20. Tubular- трубчатый
21. Wetted –(зд) - смоченный
2.Read the text and translate it into Russian
Types of fluid motion. Hydraulic fluid flow elements.
In hydrodynamics, considering the laws of motion of the liquid in the pipes, ducts and porous bodies, as well as issues of fluid flow around bodies.
The distinctive and most significant feature is the ability to move the fluid of its particles relative to each other. Moving fluid as resting, it is subject to external mass forces. However, in the moving fluid also necessary to consider the frictional force (viscosity). Quantities characterizing the state of a moving fluid is its rate of flow and pressure. The main objective of hydrodynamics - to establish the relationship between a given system of external forces acting on the moving mass of the liquid.
Consider drain of fluid from the hole made in the wall of the tank. Let level therein is maintained constant. In this case, the fluid flows with the same speed, the jet takes time quite certain position does not change, and the pressure at each point of the liquid does not change. Such fluid motion is called steady. So steady fluid motion - it is a movement in which the speed and the pressure at any point in space occupied by the liquid, do not change over time.
If the fluid level in the reservoir is not maintained all the time and decreases the liquid jet changes its position in space and the fluid pressure is also changed, this movement of fluid is unsteady. Thus, the unsteady motion of the fluid - is a movement in which the rate and pressure at any point in space occupied by the liquid, change over time.
The movement of fluid with free surface is called a gravity-flow (rivers, canals). The fluid motion without the free surface is called Pressure (in the pipe).
In order to simplify calculations of hydraulics fluid motion is replaced by a simplified scheme. The main element of the hydraulic flow model is an elementary stream. To determine it, we introduce the necessary concepts.
The curve, which describes the fluid particle during its motion is called the particle trajectory. Line current is called imaginary curve drawn in the liquid, so that each particle of the liquid contained therein at a given time, a speed that coincides with the direction of the tangent to this curve. (Fig. 1). Mentally draw line current through each point of the closed loop with small isolated in fluid (Figure 2). The resulting tubular surface called tube of current.
Liquid filling up tube of current, forms a stream of elementary. Cross-sectional area of the elementary streams, the normal direction of the current lines, called a tubular, and designated S. Since the open area is very small streams, the speed of the fluid at different points in the cross section can be regarded as equal to each other and call them as speed of the liquid in the stream, denoted υ.
Elementary volume (or mass) flow rate is the volume (or weight) of fluid flowing through a section of streams per unit time. Unit mass flow - kg / s, the unit of the volume flow - m³ / s.
One of the values that characterize the geometry of the flow is the wetted perimeter.
Æ wetted perimeter is the length of that part of the border live section through which the flow-limiting contact with the wall.
The ratio of the area S of the living section to the wetted perimeter æ called hydraulic radius of the section.
R = S / æ
3.Answer to the question on the text
1. What is the main problem of hydrodynamics? 2. What is the steady motion of the fluid? 3. How formed elementary stream?
4.Translate these sentences into English\
1.Основная задача гидродинамики - установить взаимосвязь между течением и давлением при заданной системе внешних сил, действующих на движущу -юся массу жидкости. 2 Движение жидкости со свободной поверхностью на- зывается безнапорное. 3. Одной из величин, характеризующих геометрию потока, является смоченный периметр. 4. Жидкость, заполняющая трубку тока, образует элементарную струйку.
Topic 2.1. The structure and components of hydraulic drive.
1.Before reading the text, read the words and phrases from it.
1. Hydraulic drive - гидропривод
2. Liquid supply – подача жидкости
3. Consumer - потребитель
4. Lubrication- смазывание
5. Metalworking fluids of machine tools- смазочно- охлаждающие жидкости металлорежущих станков
6. Working fluid line- трубопровод с рабочей жидкостью
7. Set in motion – приводить в движение
8. Pressurized fluid – жидкость под давлением
9. Accumulator tank - гидроемкость
10. Link- звено
11. Valve- клапан
12. Throttle- дроссель
13. Allocator- распределитель
14. Overlapping- перекрытие
15. Heat exchangers- теплообменные аппараты
16. Vent- воздухоспускное устройство
17. Hydraulic tank - гидробак
2.Read the text and translate it into Russian
2.1.1General information on hydraulic drives.
In modern technology, mainly used hydraulic drives of two types:
- Hydraulic drives for liquid supply;
- Hydraulic actuators.
For hydraulic drives, providing fluid supply to the consumers, characterized by absence of devices which convert fluid energy to mechanical work.
Such hydrostatic drives include: water supply and water heating of buildings, liquid cooling and lubrication of various machines, as well as the supply system of metalworking fluids of cutting machine .
The hydraulic drive is the set of devices designed for mechanical power transmission and transformation of movement through the working fluid. The power of the hydraulic drive consists of a pump, hydraulic motor and connecting the working fluid line.
Volume hydraulic drive is the set of devices, which include one or more of volume hydraulic motors. Volume hydraulic driver designed for set in motion driving machines and mechanisms operating by a pressurized fluid.
The hydraulic drive includes the following devices: pumps, volume hydraulic motors, hydraulic equipment, air conditioning working fluid, accumulator tank and hydraulic lines.
Pumps (volume and dynamic) create a flow of the working fluid by converting mechanical energy causing the hydraulic motor.
Volume hydraulic engines (hydraulic cylinders, hydraulic motors or rotary motors) convert hydraulic energy working fluid to mechanical energy output links of the drive.
Hydraulic equipment (valves, throttle, allocator) is designed to change direction and flow characteristics of the working fluid as well as to open or overlapping individual hydraulic lines.
Air conditioning working fluid designed to obtain the necessary quality indicators of the working fluid. These include filters, heat exchangers and, vent device.
Accumulator tank (hydraulic accumulators and hydraulic tanks) intended to contain therein a working fluid to use it in the process of work of the hydraulic drive.
Hydraulic lines are designed to move the working fluid from one hydraulic device to another.
3.Answer to the question on the text
1. What systems belong to hydrostatic drives? 2. What function is performed by the pumps? 3. What is volume hydraulic drive and what it is used for?
4.Match the information in the table and write down sentences
| Names of devices | Their functions |
| 1) Volume hydraulic drive | a) intended to contain therein a working fluid to use it in the process of work of the hydraulic drive.
|
| 2) Air conditioning | b) convert hydraulic energy working fluid to mechanical energy output links of the drive.
|
| 3) Accumulator tank | c) designed for set in motion driving machines and mechanisms operating by a pressurized fluid.
|
| 4) Hydraulic equipment | d) designed to obtain the necessary quality indicators of the working fluid. These include filters, heat exchangers and, vent device.
|
| 5) Volume hydraulic engines | e) is designed to change direction and flow characteristics of the working fluid as well as to open or overlapping individual hydraulic lines. |
|
|
|
2.2.1. Function and classification of hydraulic machines. Main parameters.
1.Before reading the text, read the words and phrases from it.
1.Liquid medium- жидкая среда
2. Fluid flow- поток жидкости
3. Inmates -заключенный
4. Driven node- ведомый узел
5. Displacement- вытеснение
6. Working chamber- рабочая камера
7. Displacers – вытеснители
8. Pistons - поршень
9. Gear wheel -шестерня
10. Plate- пласитна
11. Volumetric –объемный
12. Alternately communicating- попеременно сообщающийся
13. Flow- проточный
14. Sealed- герметичный
15.Efficiency factor- КПД
2.Read the text and translate it into Russian
Function and classification of hydraulic machines. Main parameters.
The main elements of hydro systems are hydraulic machines. Hydraulic machine is a device that creates or uses the flow of the liquid medium.
By means of this device, it happens converting of mechanical energy into energy of fluid flow or using working fluid flow for useful work. To hydraulic machines relate pumps and hydraulic engines.
Pump is a machine to create a flow of liquid medium.
Hydraulic engine is a machine designed to convert energy in working fluid flow into energy of motion of the output link.
In the volume hydraulic machines, the energy in mates in the flow of the liquid is transferred to the driven node due to the static pressure of the liquid.
As used in hydraulic drive of rotary volume pumps and hydraulic motors displacement of the working fluid going in the result of the displacement of its from the working chambers using displacers carried out in the form of pistons, gear wheel, plates and so on.
Classification of hydraulic machines.
All hydraulic machines are divided into two main types: dynamic and volumetric. In the dynamic hydraulic machine fluid medium moves under force action on it in the chamber constantly communicating with the input and output of the pump. In the volume hydraulic machines fluid moves by periodic changes of volume the chamber it occupies alternately communicating with the input and output of the pump.
Dynamic hydraulic machine can also be called "flow" because it has inner flow cavity which is always connected to the input and output, and volume - "hermetic" because it has a sealed working chamber, which can be connected at a given time, or only to the input or output of the hydraulic machine. This means that in the volume hydraulic machines entrance area is always disconnected from the output. Workflow of volume hydraulic machine is in the force interaction of the working fluid and displacing hydraulic machine. Large velocity of motion fluid and working bodies of the bulk hydraulic machine thus in principle not required, because pressure played fundamental role in the working process .
The main parameters of hydraulic machines.
The main parameters of volume pumps and hydro motors are: the volume of the working chamber (V0), flow (Q), the discharge pressure (Pн), torque (M), power (N), and the volume (η ов) and mechanical (ηmeh) to efficiency factor (EF).
The dependence of the flow Q pump from pressure Pн, at all other things being equal (speed, temperature, fluid viscosity and so forth.) called the characteristic of the pump Q = f (p), otherwise the pump characteristic is a graphical dependence of its main technical indicators from pressure.
The main parameters
| № | Parameter name | Symbol | Unit of measure | Determination | Formula |
| 1 | The volume of working chamber | V0 | м3 | Closed space communicates alternately with the pump suction and discharge cavity | V0- calculated by the design |
| 2 | The flow | Q | м3 с | Amount of liquid supplied by pump per unit time | Q = V0 n |
| 3 | Injection pressure | P | Па | Hydraulic power inmate in a fluid stream |
|
| 4 | The power | N | Bт | This power is transmitted pump fluid | N = Q P |
| 5 | EF | η | % | The ratio of useful power to shaft power |
|
| 6 | Shaft rotation frequency | n | turns in a minute | It is the frequency of motor revolutions per time unit | n- depends on the design of the engine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.Answer to the questions on the text
1. What is Hidro mashine? 2. What is a principle of work hydraulic motor? 3. How many types of hydraulic machines and what are they?
4.Translate these sentences into English\
1.Насос это машина для создания потока жидкой среды. 2. Основными элементами гидросистем являются гидромашины. 3. В объемных гидромашинах входная область всегда отсоединена от выходной. 4. Гидродвигатель это машина, предназначенная для преобразования энергии потока рабочей среды в энергию движения выходного звена.
5.Turn the table into Russian (переведите данные таблицы на русский язык)
2.3.1. Purpose of devices. Classification. Main parameters.
1.Before reading the text, read the words and phrases from it.
1.Flow rate- расход
2.Adjusting (adjustable)- регулирующие (регулируемые)
3.Guiding- направляющие
4.Partially- частично
5.Overlap- перекрытие
6.Flow area- проходное сечение
7.Flow section- сечение потока
8.Consumption- расход
9.Shut-off control element- запорно- регулирующий элемент
10.Customizable-настраиваемые
11.Spring preload- поджатие пружины
12.Disassembly- разборка
13.Mounting –присоединительный
14.Drainage fluid removal –дренажный отвод жидкости
15.Conditional pass -условный проход
2.Read the text and translate it into Russian
Purpose of devices. Classification. Main parameters.
Hydroapparats are devices intended for changing or supporting the defined parameters of the flow of the working fluid (pressure, flow rate, direction of movement). By the nature of performing their functions, all Hydroapparats divided into adjusting and guiding.
Adjusting is a Hydroapparat, wherein the changing of the parameter of fluid flow occurs by partially opening or partially the flow cross section therein.
Guiding is a Hydroapparat, that changes the direction of working fluid flow through the full opening or full overlap flow area therein.
Under flow area of Hydroapparats understood flow section, area of which determines consumption of the working fluid passing through the Hydroapparats .
The main element of Hydroapparats is shut-off control element - the item, if you move that partially or completely blocked flow area of Hydroapparats .
Construction shut off element.

valve the spool crane
Hydro apparatuses are adjustable and customizable.
Adjustable is a Hydro apparatus, the characteristics of which (flow area, spring preload, and others.) сan be changed by a signal from the outside during operation of the hydraulic system.
Customizable is a Hydro apparatuses , the characteristics of which can be changed only in a broken hydraulic system. To do this, usually require disassembly of Hydro apparatus.
Classification of Hydro apparatus presented on picture 1.
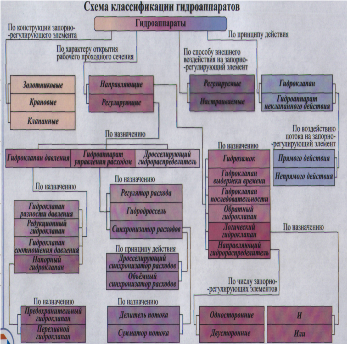
In principle, and the semi constructive schemes of Hydro apparatus, their mounting holes represent by letters of Latin alphabet: P-hole for supplying pressurized hydraulic fluid; A and B - holes for attachment to other hydraulic devices; T- hole for discharging the working fluid in the tank; X and Y –holes for flow control; L- hole for drainage fluid removal.
To the main parameters of Hydro apparatus relate:
Conditional pass is the diameter of such conditional hole, an area of which is equal to the maximum value of the flow areas Hydro apparatus .
Nominal pressure Рном - is the highest fluid pressure in the supplied stream in which Hydro apparatus must operate within a set of the resource while saving its parameters within the established norms.
Nominal flow rate Qном - is a flow rate of fluid with a certain viscosity, passing through the Hydro apparatus in which it performs its function while saving parameters within the established norms.
Selecting a specific Hydro apparatus for hydro system make by the size of the conditional pass, checking the compliance with the calculate value of the maximum working fluid flow through Hydro apparatus and the maximum working pressure the passport data of Hydro apparatus.
All hydro apparatuses are used in volume hydraulic drive can be divided into three main classes: Hydraulic chokes, hydraulic valves and hydraulic distributors.
3.Answer to the questions on the text
1. What do hydro apparatuses do you know? 2. Which is a key element of hydro apparatuses? 3. Which refers to the basic parameters of hydro apparatuses?
4.Translate these sentences into English.
1.Регулируемый- это гидроаппарат, характеристики которого могут быть изменены по сигналу извне во время работы гидросистемы. 2. Гидроаппаратами называются устройства, предназначенные для изменения или поддержания заданных параметров потока рабочей жидкости. 3. Неработающая система требует разборки гидроаппарата. 4. Под проходным сечением гидроаппарата понимается сечение потока , площадь которого определяет расход рабочей жидкости, проходящей через гидроаппарат.
5. Translate notations in the table on the picture 1 in English
(переведите схему классификации гидро аппарата на рис.1 на английский язык)
2.6.1. Conformation and operation of the piston compressor.
1.Before reading the text, read the words and phrases from it.
1.Conformation- устройство
2.Piston(reciprocating ) compressor- поршневой компрессор
3.Air sucking (intake)- всасывание воздуха
4.Suction line- линия всасывания
5.Intake valve- всасывающий клапан
6.Delivery- нагнетательный
7.Pushed out -выталкивается
8.Area charts- площадь диаграммы
2.Read the text and translate it into Russian
Conformation and operation of the piston compressor.
In the pneumatic networks in engineering are used compressed air pressure up to 1 MPa. To produce the compressed air compressors of various types are used. Compressors are machines for the compression of air or other gases. The practice of using compressors has shown that for the machine industry with the need for compressed air up to 20,000 m³ / h and pressures up to 0.7 MPa is the rational use of reciprocating compressors.
Theoretical process to consider the operation of the compressor double action (picture1). Compressor circuit diagram of a double-acting and feed one side of the compressor.
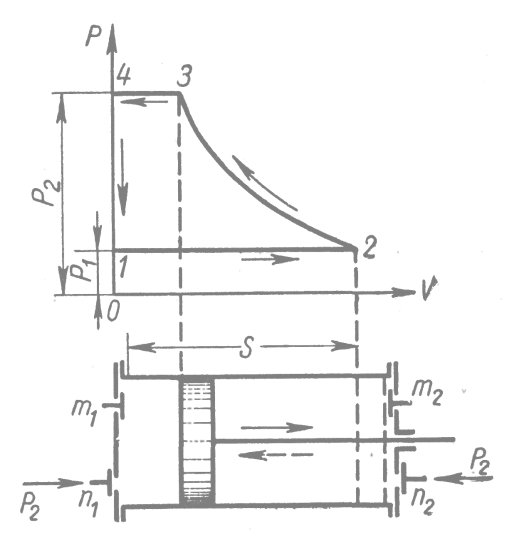
During the course of the piston right through the valve m1 is sucked air; pressure in the cylinder throughout the stroke constant and equal to atmospheric pressure. Therefore, the line 1-2 in figure parallel to the abscissa called suction line. During the return stroke of the piston m1 left intake valve is closed and the air in the cylinder is compressed. Line 2-3 is called a line of compression. Pressure increases due to a decrease of air volume, as left n1 delivery valve is still closed. When the compression pressure reaches P2 n1 delivery valve opens and compressed air at the same pressure P2 is pushed out from the cylinder. Line 3-4 is called a delivery line.
After the injection, if it is assumed that in the cylinder there is no air, suction starts again.
Area charts 1-2-3-4 called indicatorб expresses the work of one cycle of the compressor expended on suction, compression and delivery of air.
Upon cooling of the cylinder the compression is by polytropic process.
3.Answer to the questions on the text
1.What is the compressor? 2. Describe the principle of operation of the double-action compressor.
4.Translate these sentences into English.
1. Для выработки сжатого воздуха применяют компрессоры различных типов. 2. По окончании нагнетания, если считать что в цилиндре не остается воздуха. Снова начинается всасывание. 3. При охлаждении цилиндра сжатие происходит по политропному процессу. 4. Давление увеличивается вследствие уменьшения объема воздуха.
Использованная литература
А.В.Лепёшкин, А.А.Михайлин. Гидравлические и пневматические системы: учебник для среднего профессионального образования/А.В.Лепёшкин, А.А.Михайлин; Под ред. Ю.А.Беленкова.- М.: Издательский центр «Академия», 2004.- 336с.
Гидравлика, гидромашины и гидропневмопривод: учеб.пособие для студентов высш.учебных заведений/ Т.В.Артемьева, Т.М.Лысенко, А.Н.Румянцева, С.П.Стесин; под ред. С.П.Стесина.- 4-е изд., стер.- М.: Издательский центр «Академия», 2008- 336с.
24


 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход















 Методическое учебное пособие по английскому языку интегрированное с дисциплиной гидравлика "Чтение для получения информации" (2.32 MB)
Методическое учебное пособие по английскому языку интегрированное с дисциплиной гидравлика "Чтение для получения информации" (2.32 MB)
 0
0 1721
1721 121
121 Нравится
0
Нравится
0


