John: Dora, why are you dressed like that?
Dora: I’m playing a fortune teller in the school play next week. Come on, I’ll tell you your fortune.
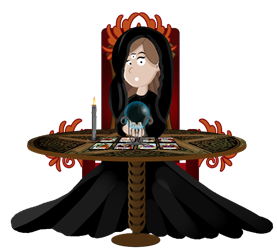
In ten years’ time you’ll be managing your own company. You’ll be making the best computer games in the world! You’ll be rich and famous! In twenty years you’ll have conquered the world.
John: Great! Can you see the nearer future, too?
Dora: Oh, yes! You’re a kind young man, John. And very generous, too. You are going to give money someone very soon.
John: Really? When?
Dora: Now. Betty and I are going to the cinema tonight and I’m broke. Will you lend me ten pounds?
John: Of course, I will. In ten years’ time!
Dora: Oh, how funny! Ha! Ha! Ha!
So, look at the highlighted forms in the dialogue. What are they?
am playing – Present Continuous Tense
will tell/ will be / Will you lend…? are the Future Simple forms
will be managing / will be making – Future Continuous Tense
will have conquered – Future Perfect Tense
are going to – construction to be going to
What do you think all these forms are used for in the dialogue?
Right, for expressing future actions.
In this lesson we’re going to look at the most common ways of expressing the future in English:
1. Future Simple
2. Present Simple
3. Present Continuous
4. And the construction to be going to (inf)
We’ll revise their formation and you’ll get to know in what situation to use them.
So, let’s get started.
First, let’ s revise the formation of Present Simple/Present Continuous/Future Simple and the construction to be going to.
Complete the tables.
Future Simple
|
will + infinitive |
|
|
Positive |
He will be a famous businessman. They will come tomorrow. |
|
Negative |
He will not (won’t) be a famous businessman. They will not ( won’t) come tomorrow. |
|
Question |
Will he be a famous businessman? Will they come tomorrow? |
The Future Simple is formed with the help of will + infinitive.
Be going to
|
am/is/are going to |
|
|
Positive |
He is (‘s) going to give her some money. We are (‘re) going to the cinema tonight. |
|
Negative |
He is not (isn’t) going to give her some money. We are not (aren’t) going to the cinema tonight. |
|
Question |
Is he going to give her some money? Are we going to the cinema tonight? |
Remember! The verb to be has three forms am/is/are.
Present Continuous
|
am/is/are + verb + ing |
|
|
Positive |
She is taking part in a play next week. |
|
Negative |
She is not (isn’t) taking part in a play next week. |
|
Question |
Is she taking part in a play next week? |
Present Simple
|
V / V(s/es) |
|
|
Positive |
Our train leaves at 9.30. The doors open at 8 am. |
|
Negative |
Our train does not (doesn’t) leave at 9.30. The doors do not (don’t) open at 8 am. |
|
Question |
Does our train leave at 9.30? Do the doors open at 8 am? |
We form the Present Simple with the first form of the verb. we usually add -s(-es) to the third person singular. In questions and negative sentences, we use do/don’t with I/we/you/they and does/doesn’t with he/she/it.
Future Simple is used for:
on-the-spot decisions.
For example:
We haven’t got any juice. I’ll go to the corner shop and get some.
It’s cold in here. I’ll turn on the heating.
for predictions based on what we think, believe or imagine. Especially with: I expect, I believe, I’m sure, I’m afraid, probably, etc.
For example:
I think they’ll agree to our plan.
I hope, he will like his birthday present.
for actions which we cannot control but which will definitely happen.
The baby will be born in the new year.
to make a request.
Will you do me a favour?
Will you lend me ten pounds?
to promise to do something.
Don’t worry. I’ll fix your bike tomorrow.
Be going to is used for:
predictions based on what we can see or what we know, especially when there is evidence.
For example:
Look! The driver has lost control of the car. He’s going to crash!
That boy is going to climb a tree.
for intentions, plans or ambitions for the future.
They are going to get married next month. (they have already decided to do it.)
She is going to keep to a diet.
We use the Present Continuous:
to talk about fixed arrangements and plans in the near future.
For example:
I’m having dinner with Betty this evening. (It’s a date.)
She’s leaving tomorrow.
Present Simple
We use the present simple to talk about timetables/ programmes or scheduled events.
For example:
The concert begins at 8.30.
The next bus goes to the town center.
The boat leaves at 8 o’clock in the morning.
Now it’s time to practice the rule.
Read the sentences and choose the ideas expressed in them.
A. a promise
B. I think this will happen
C. intention to do something
D. an on-the-spot decision
E. an offer
F. a prediction based on what I see
1. Granny’s said she is not feeling very well.
Oh, dear. I’ll visit her straight after work then. (D. an on-the-spot decision)
2. In the future people won’t need reading glasses. We’ll all have laser eye surgery. (B. I think this will happen)
3. You’re playing badly, today. I think you are going to lose this game. (F. a prediction based on what I see)
4. I know you don’t believe me, but I’ll work really hard this time. (A. a promise)
5. I’m going to finish this report today even if I have to stay up all night!
(C. intention to do something)
6. I can’t lift this suitcase. It’s too heavy.
It’s all right, Mary. I’ll help you to carry it. (E. an offer)
That’s all for today.
Hopefully the lesson was useful and informative to you, guys!
Practice your grammar skills because practice makes perfect!

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход


 0
0 2241
2241


