Муниципальное автономное общеобразовательное учреждение –
средняя общеобразовательная школа № 7
Октябрьский район, г.Екатеринбург
Урок английского языка для учащихся 9-11 классов на тему :
"Space Exploration"
Выполнил:
Шишкина Татьяна Николаевна
Учитель английского языка МАОУ СОШ №7
ВКК
г.Екатерин
English lesson"Space Exploration"
![]()
Урок английского языка «Исследование космоса» разработан для старших классов средней школы и приурочен к 50 годовщине полета Юрия Гагарина в космос. Данный урок предоставляет основные сведения, которые должны знать учащиеся об исследовании космоса, помогает закрепить полученные знания и уметь рассуждать на эту тему на английском языке.
Grade:8-11
Subject: English
Theme: “Space exploration”
Materials: Cards for different activities, board, lesson plan, Power Point presentation.
Primary aims:
1.Reviewing useful lexis of the theme and practice it by using in different speaking situations .Consolidation and extension of knowledge about Russian Space and its main heroes. To implement some activities requiring critical thinking skills(comparing, contrasting ,generalizing),matching ,pair discussions.
2.To extend writing skill, integrating practice exercises with pronunciation work; extend sts` vocabulary, listening and writing skills, focus on problem sounds and word stress ,using more complex situations.
3.To increase and develop sts` motivation and interest, as well as to reduce anxiety and lower inhibition, to rise the level of ability to cope with difficult tasks and speaking situations.
Propositions of the lesson:
1.To work with communicative grammar practice activities ,vocabulary extension activities.
2.To work on listening ,speaking ,reading and writing ,using integrated approach to pronunciation, including learner-training and revision.
3.To execute different activities ,using tables and charts, focusing more on students being active and speaking independently.
Intersubject`s relations: Spoken English, Astronomy, Russian History and Phonetics.
Procedure of the lesson:
Pre-lesson activities (Teaching conversation)
“Match the word” activity (increase sts’ vocabulary)
Checking up the homework-Story about great Russian Inventors(Speaking activity)
“True-false” statements-checking the understanding
“Identify the words” activity- (increasing vocabulary of this theme)
LESSON “SPACE EXPLORATION”
Organization moment: Explanation the theme and the main targets of the lesson, tell some words about the lesson procedure.
Good Morning, dear friends! Today we are having an unusual lesson. The topic of the lesson is "Space exploration”. We've got much work to do today. We'll remember some facts from the history of space exploration, you'll tell us what you know about planets of Solar System, you are going to do some exercises and of course we'll learn much interesting about Russian scientists and astronauts.
1.Pre-lesson activities: Students have to answer teacher’s questions about historical moments of Space Exploration. Conversation T-S1-S2-S3
T: Dear students, I want you review some facts from Russian history and answer some questions about Space Exploration .
Who was the first man to fly into space?
Who was the first woman to fly into space?
Who was the first astronaut to walk on the Moon?
Who was the first man to leave a spaceship for a spacewalk?
How many planets are there in the Solar System?
6. Can we say that space exploration is the main part of science?(this question supposes giving sts’ opinion)
(Give some speaking modules for this question, such as-
To my mind…..
In my opinion…..
As for me, I consider that…..
2.Vocabulary: . Students have to match the combinations of words, which are written on the blackboard after 3 minutes.
|
|
3. Speaking.(checking up the homework)
Teacher asks students to read (or to retell) the information about most famous and prominent Russian scientists and cosmonauts and shows the presentation about them:
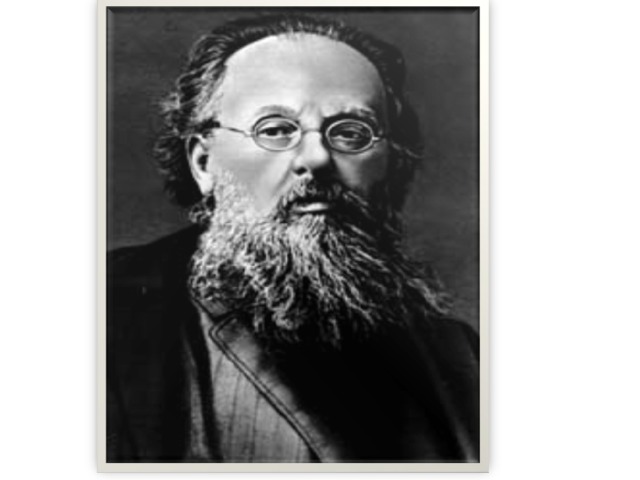
1) Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky – the founder of astronautics in Russia, put forward several ideas about space travel. Tsiolkovsky’s idea of spaceship was based on the use of liquid fuels. His calculations were used in modern theory of cosmonautics and practical space travel.
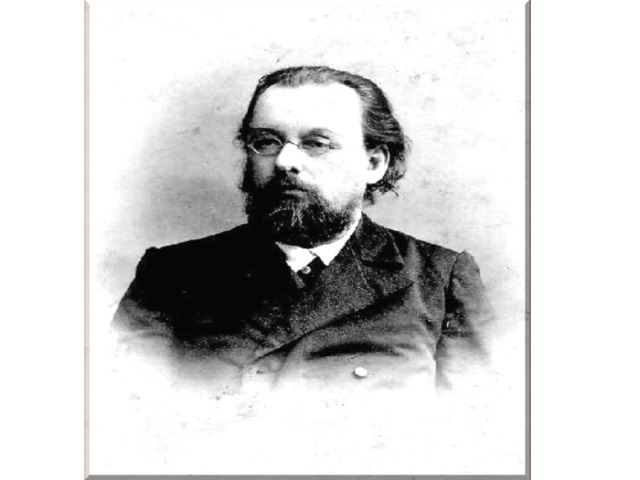
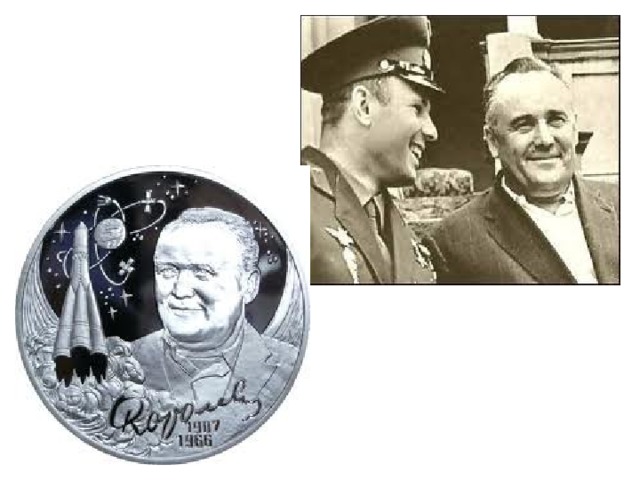
2) Sergei Pavlovich Korolyov- is a famous scientist and founder of practical cosmonautics. He was the chief constructor of the first Earth sputniks and spaceships. Then followed rockets to the Moon, Mars,Venus.
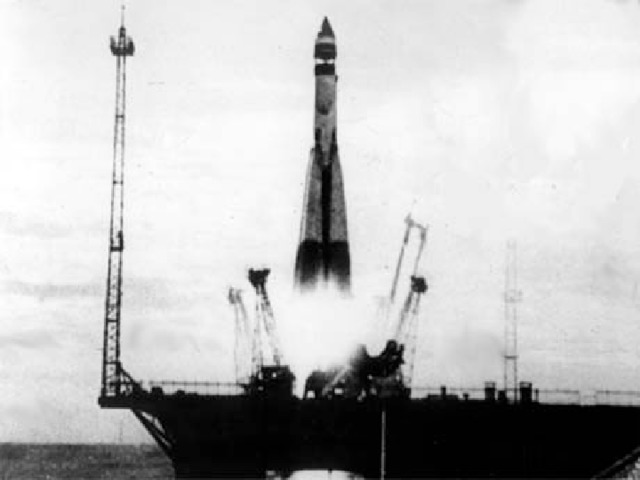
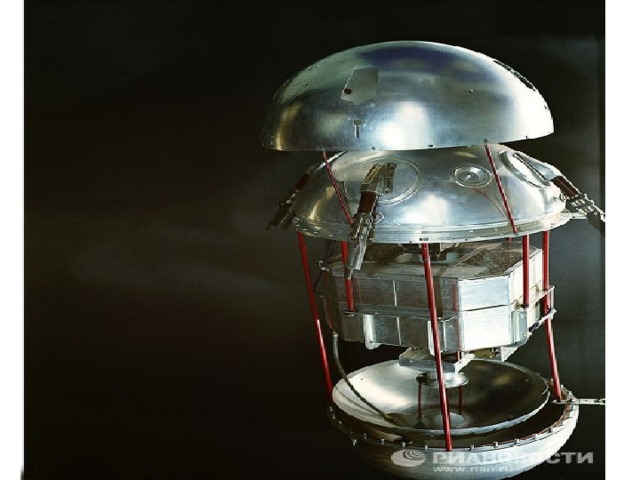
3) The space age began on October 4, 1957. On that day, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to circle the earth. Its capsule weighing 83.6 kilograms went into Earth orbit carrying a radio transmitter whose “bleeps” (pips) were received on the ground.
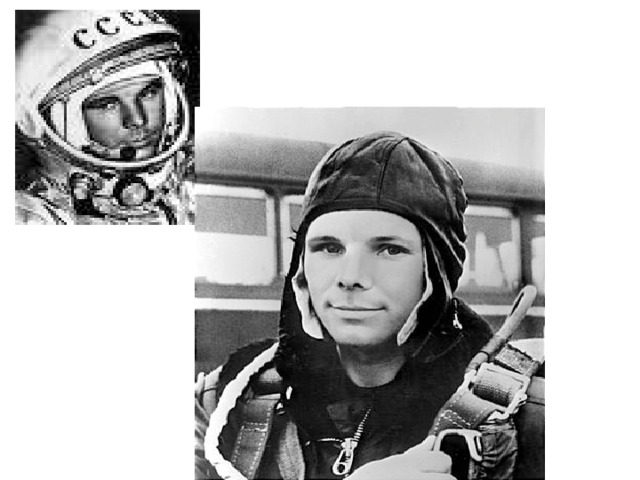
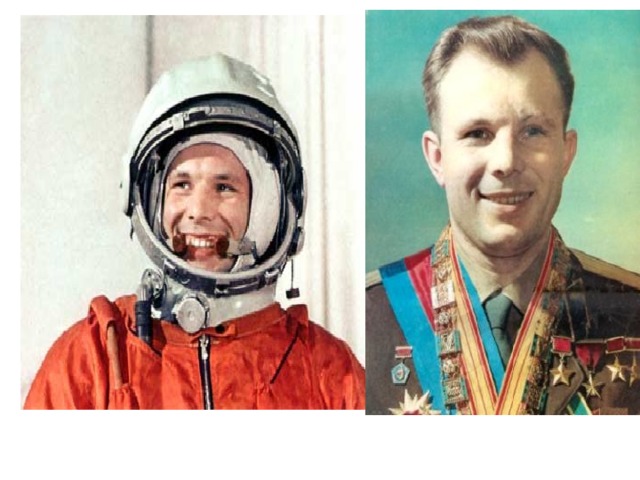
4) Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin, a Soviet air force pilot, was the first human to travel in space. The Soviet cosmonaut circled the earth on April 12, 1961. From blastoff to landing, his trip around the earth lasted 1hour and 48 minutes. The news about space flight of the Soviet cosmonaut immediately flew over the world.
5) Valentina Tereshkova was the first woman-cosmonaut in the world. From June 16 until June 19, during a group flight with V.Bykovsky, the spaceship “Vostok-6” piloted by Tereshkova made in 70 hours and 41 minutes 48 circuits around the earth, covering a distance of about 2 million kilometers.
When she was in space, she was there together with her “space-brother” Valery Bykovsky.
This was another great achievement – launching two spaceships at the same time.
6) In 1965 the cosmonaut Alexei Leonov went outside wearing a space suit connected to the capsule by a line which also carried his oxygen supply, becoming the first person to “walk” in space. From the first experiments scientists went over to systematic exploration of space.
7) The gravity of Earth continually pulls on our bodies to give us weight. But if you are in a lift that is speeding downwards, you feel lighter. This effect is exaggerated in a spacecraft: as it is falling in a gravitational field, the astronauts inside it are falling at the same rate and become weightless.
4. “True-False statements”. Students have to correct the wrong statements.
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky – the founder of astronautics in Great Britain, put forward several ideas about space travel.
Sergei Pavlovich Korolyov was the chief constructor of the first telephone.
On October 4, 1967 the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to circle the earth.
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin, a Soviet air force pilot, was the first human to travel to Mars.
Valentina Tershkova was the first woman-cosmonaut in the world.
Alexei Leonov went outside wearing a space suit connected to the capsule by a line which also carried his oxygen supply, becoming the first person to “walk” in space.
Key: 1- false, 2- false, 3- false, 4- false, 5- true, 6- true.
5. “ Identify the words” Students have to read definition of active words from little pages which they pull and find them in the list of words.
1. It is a space and everything that exist in it. (the universe)
2.It is a huge group of stars and planets. (galaxy)
3.It is a place far above the Earth where there is no air. (a space)
4.It is a rocket or other vehicle that can travel in space. (a spaceship)
5.It is a large, round object that goes round a star. (planet)
6.It is the Sun together with the planets going round it. (the Solar System)
7.to make, design, or think of new type of thing (invent)
.the act of traveling through a place in order to find out about it (explore)
8.It is a huge group of stars and planets. (galaxy)
9.the tools, machines, clothes that you need to do a particular job or activity (equipment)
6. Reading: Read the text and try to get the most interesting facts for you:
SPACE EXPLORATION
Space travel is humanity’s greatest adventure – the chance to explore the moon, the planets, and the stars. The space age began on October 4, 1957. On that day, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to circle the earth. The first manned space flight was made on April 12, 1961, when a Soviet cosmonaut, Yuri Gagarin, orbited the earth in a spaceship. During the years that followed this first space expedition, many flights carried people into space.
Human beings first set foot on the moon on July 20, 1969. U.S. astronaut Neil A.Armstrong stepped out of the Apollo 11 lunar module, “Eagle”. For about two hours he and Edwin E.Aldrin explored near the module and set up experiments. During the years since the space age began, many uses for space travel have been discovered. The space age developed a huge industry called the aerospace industry to design and build space equipment. A new field of medicine called space medicine came into being to study the problems of living and working in space. Weather forecasts receive warning of storms with pictures taken by weather satellites. Telephone calls and television pictures are sent around the world by communications satellites. Signals from navigation satellites enable ship navigations and search and rescue forces to determine their positions with great accuracy. Scientific satellites and space probes discovered the Van Allen radiations belt around the earth and made many other discoveries. Earth survey satellites, used for detecting mineral deposits, diseased crops, sources of pollution, and map-making; military satellites, used mainly for reconnaissance and intelligence gathering; and astronomical satellites, which are observatories in space, orbiting above the blanketing layer of the Earth’s atmosphere. During the early years of the space age, success in space became a measure of a country’s leadership in science, engineering, and national defense. As a result, the Soviet Union and the United States competed with one another in developing their space programmers. But both nations began to realize that they could benefit from working together. In 1975, the S.U. and U.S. cooperated in their first joint space mission “Soyuz-Apollo”. The principal area of cooperation between U.S. and Soviet space programmers has been in space medicine.
People have always wanted to explore the unknown. Mankind always dreamed of overcoming gravitation and reaching other planets. Among the achievements we may enumerate the landing of automatic stations on the Moon, the flights of space laboratories towards the Venus and Mars. During the years that followed this first space expedition, many flights carried people into space. There are manned and unmanned spacecraft (carry instruments and radio equipment)A reusable manned spacecraft is called a shuttle. The first astronauts were sent into space in small capsules that sat on top of rockets. These missions were expensive as the rockets could only be used once. The main parts of the Shuttle – the orbiter spacecraft, and the rocket boosters – are reusable. The orbiter returns to Earth like a plane, and can be used over and over again. The first space station, Salyut 1, was launched in 1971, and was visited by the Soyuz for 23 days.
By 1983 six more Salyut craft had been launched and cosmonauts were staying longer and longer in orbit. In 1983 and 1985 large Cosmos unmanned craft were automatically docked with Salyut 7, making it into a large space station. From the space station a detachable descent module could carry materials and experiments back to Earth.
In 1986 the Soviets launched “Mir”, the central module of a new space station far more complex than Salyut. As with Salyut, Mir was designed to receive both manned Soyuz craft and unmanned Progress cargo craft.
Answer the questions:
Why is the travel humanity’s greatest adventure?
When did the space age begin?
What country launched the first artificial satellite to circle the earth?
When was the first manned space flight made?
When did human beings first set foot on the moon?
What industry did the space age develop?
In what way are satellites used today?
How do nations do scientists hope to answer with the help of space exploration?
What kinds of spacecraft do you know?
Is shuttle a reusable vehicle
Reflection and giving the homework: Express the same in English:
Космическая эра началась с запуска первого спутника Земли.
Американские астронавты исследовали Луну и проводили эксперименты.
Спутники позволяют получать нужную для человека информацию.
Среди достижений последних лет можно отметить запуски зондов на другие планеты.
Современные космонавты месяцами живут на космических станциях и регулярно выходят в открытый космос.
USED INTERNET SOURSES:
http://www.nasa.gov National Aeronautics and Space Administration
http://www.esa.int - European Space Agency
http://www.federalspace.ru/ Russian Space Agency
http://space.skyrocket.de/
http://www.planet4589.org/space/
http://www.spacefacts.de
http://www.space.com
Екатеринбург 2001
ACTIVITIES:
1.Vocabulary: . You have to match the combinations of words, which are written on the blackboard after 3 minutes.
|
|
3. Speaking.(checking up the homework)
Teacher asks students to read (or to retell) the information about most famous and prominent Russian scientists and cosmonauts and shows the presentation about them:
1) Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky – the founder of astronautics in Russia, put forward several ideas about space travel. Tsiolkovsky’s idea of spaceship was based on the use of liquid fuels. His calculations were used in modern theory of cosmonautics and practical space travel.
2) Sergei Pavlovich Korolyov- is a famous scientist and founder of practical cosmonautics. He was the chief constructor of the first Earth sputniks and spaceships. Then followed rockets to the Moon, Mars,Venus.
3) The space age began on October 4, 1957. On that day, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to circle the earth. Its capsule weighing 83.6 kilograms went into Earth orbit carrying a radio transmitter whose “bleeps” (pips) were received on the ground.
4) Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin, a Soviet air force pilot, was the first human to travel in space. The Soviet cosmonaut circled the earth on April 12, 1961. From blastoff to landing, his trip around the earth lasted 1hour and 48 minutes. The news about space flight of the Soviet cosmonaut immediately flew over the world.
5) Valentina Tereshkova was the first woman-cosmonaut in the world. From June 16 until June 19, during a group flight with V.Bykovsky, the spaceship “Vostok-6” piloted by Tereshkova made in 70 hours and 41 minutes 48 circuits around the earth, covering a distance of about 2 million kilometers. When she was in space, she was there together with her “space-brother” Valery Bykovsky. This was another great achievement – launching two spaceships at the same time.
6) In 1965 the cosmonaut Alexei Leonov went outside wearing a space suit connected to the capsule by a line which also carried his oxygen supply, becoming the first person to “walk” in space. From the first experiments scientists went over to systematic exploration of space.
7) The gravity of Earth continually pulls on our bodies to give us weight. But if you are in a lift that is speeding downwards, you feel lighter. This effect is exaggerated in a spacecraft: as it is falling in a gravitational field, the astronauts inside it are falling at the same rate and become weightless.
4. “True-False statements”. Students have to correct the wrong statements.
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky – the founder of astronautics in Great Britain, put forward several ideas about space travel.
Sergei Pavlovich Korolyov was the chief constructor of the first telephone.
On October 4, 1967 the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to circle the earth.
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin, a Soviet air force pilot, was the first human to travel to Mars.
Valentina Tershkova was the first woman-cosmonaut in the world.
Alexei Leonov went outside wearing a space suit connected to the capsule by a line which also carried his oxygen supply, becoming the first person to “walk” in space.
5. “ Identify the words” Students have to read definition of active words from little pages which they pull and find them in the list of words.
1. It is a space and everything that exist in it.
2.It is a huge group of stars and planets.
3.It is a place far above the Earth where there is no air.
4.It is a rocket or other vehicle that can travel in space.
5.It is a large, round object that goes round a star.
6.It is the Sun together with the planets going round it.
7.to make, design, or think of new type of thing
.the act of traveling through a place in order to find out about it
8.It is a huge group of stars and planets.
9.the tools, machines, clothes that you need to do a particular job or activity
8.Complete the sentences using the verbs from the table:
competed, enable, developed, explored, orbited, was based, launched, receive, are transported, benefit
On that day, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ______Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to circle the earth.
But both nations began to realize that they could _____ from working together.
As a result, the Soviet Union and the United States______ with one another in developing their space programmers.
Weather forecasts ______ warning of storms with pictures taken by weather satellites.
Signals from navigation satellites_____ ship navigations and search and rescue forces to determine their positions with great accuracy.
The space age ______ a huge industry called the aerospace industry to design and build space equipment.
For about two hours Armsrong and Aldrin______ near the module and set up experiments.
Today, American astronauts ______ into space by the Space Shuttle.
The first manned space flight was made on April 12, 1961, when a Soviet cosmonaut, Yuri Gagarin, ______ the earth in a spaceship.
Tsiolkovsky’s idea of spaceship_____ on the use of liquid fuels.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











































 Разработка урока английского языка "Space exploration" 9-11 классы (11.51 MB)
Разработка урока английского языка "Space exploration" 9-11 классы (11.51 MB)
 0
0 2341
2341 205
205 Нравится
0
Нравится
0


