
Parts of speech. General classifications
By Eveline Podshivalova,
МБОУ «Горловская СОШ», Скопинский район Рязанской области

Parts of speech. General classifications
Plan
- The Parts of Speech Problem. Grammatical Classes of Words.
1.1. The Principles of Classification as used by Prescriptive Grammarians.
1.2. The Principles of Classification as used by Non-Structural Descriptive Grammarians.
1.3. The Principles of Classification as used by Structural Descriptive Grammarians.
1.4. The Classification of Words in Post-Structural Traditional Grammar
2. The System of Parts of Speech.

1. The Parts of Speech Problem. Grammatical Classes of Words.

The problem of word classification
The problem of word classification into part of speech still remains one of the most controversial problems in modern linguistics. The attitude of grammarians with regard to parts of speech and the basis of their classification varied a good deal at different times. Only in English grammarians have been vacillating between 3 and 13 parts of speech.

Four approaches to the problem of word classification into parts of speech
Classical, or logical inflectional , worked out by prescriptivists
Functional ,
worked out by descriptivists
Distributional,
worked out by structuralists
Complex

The principles of Classification as used by Prescriptive Grammarians
Prescriptive grammarians , who treated Latin as an ideal language , described English in terms of Latin forms and Latin grammatical constraints.
The underlying principle of classification was form , which, as can be seen from their treatment of the English noun, was not only morphologic but also syntactic.
Similar to Latin, words in English were divided into:
- declinables (nouns, adjectives, pronouns, verbs, participles);
- indeclinables (adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, articles).

The principles of Classification as used by Non-Structural Descriptive Grammaries. Henry Sweet (1845-1912)
Diveded word into:
1.Declinables:
- Noun-words (noun, noun-pronoun, noun-numeral, infinitive, gerund);
- Adjective-words (adjective, adjective-pronoun, adjective-numeral, participle);
- Verb (finite verb);
- Verbals (infinitive, gerund, participle).
2. Indeclinables (particles):
- Adverb;
- Preposition;
- Conjunction;
- Interjection.
Henry Sweet speaks of three principles of classification : form, meaning and function .

The principles of Classification as used by Structural Descriptive Grammaries
He rejected the traditional principle of classification of words into parts of speech replacing it with the methods of distributional analysis and substitution. Words that exhibit the same distribution belong to the same class. The distribution of a word is the position of a word in the sentence. To classify the words of English, Charles Fries used three sentences called substitution frames . He thought that the positions, or the slots, in the sentences were sufficient for the purpose of the classification of all the words of the English language.
Charles Fries (1887-1967 )

2. The System of Parts of Speech.

The Classification of Words in Post-Structural Traditional Grammar
In modern linguistics parts of speech are discriminated according to three criteria: semantic, formal and functional.

1. The semantic criterion presupposes the grammatical meaning of the whole class of words (general grammatical meaning).

2. The formal criterion reveals paradigmatic properties: relevant grammatical categories, the form of the words, their specific inflectional and derivational features.

3. The functional criterion concerns the syntactic function of words in the sentence and their combinability.

Division into notional and functional parts of speech
- noun; the adjective; the numeral; the verb; the adverb.
- noun;
- the adjective;
- the numeral;
- the verb;
- the adverb.
Notional parts of speech
- the preposition; the conjunction; the article; the pronoun; the particle; the modal words; the interjection.
- the preposition;
- the conjunction;
- the article;
- the pronoun;
- the particle;
- the modal words;
- the interjection.
Functional parts of speech

Notional parts of speech
Functional parts of speech
- Denote distinct lexical meaning;
- Perform independent syntactic function in the sentence;
- Have certain grammatical categories;
- Can be connected with each other directly or with help of the formal words.
- Words of incomplete nominative meaning and non-self-dependent
- Perform mediatory functions in the sentence
Distinguishing features of notional and functional parts of speech
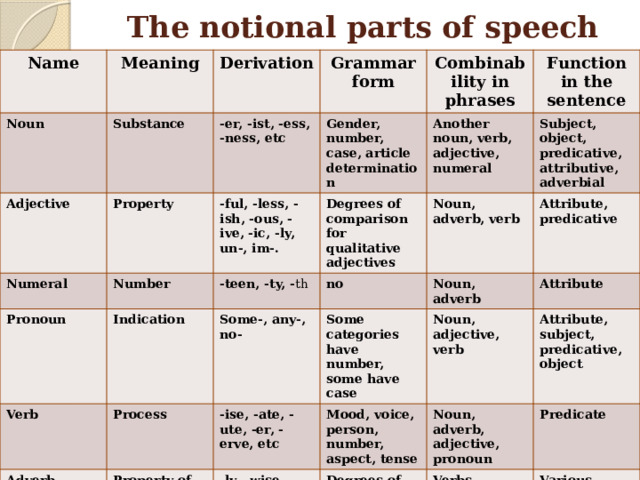
The notional parts of speech
Name
Meaning
Noun
Substance
Derivation
Adjective
Property
Numeral
-er, -ist, -ess, -ness, etc
Grammar form
Combinability in phrases
-ful, -less, -ish, -ous, -ive, -ic, -ly, un-, im-.
Number
Pronoun
Gender, number, case, article determination
Another noun, verb, adjective, numeral
Degrees of comparison for qualitative adjectives
Verb
Indication
-teen, -ty, - th
Function in the sentence
Process
Some-, any-, no-
Adverb
Noun, adverb, verb
no
Subject, object, predicative, attributive, adverbial
Property of process or another property
Some categories have number, some have case
-ise, -ate, -ute, -er, -erve, etc
Statives
Noun, adverb
Attribute, predicative
Noun, adjective, verb
Different states, mostly temporary
Mood, voice, person, number, aspect, tense
-ly, -wise, --ways, --ward(s)
Attribute
Degrees of comparison for qualitative adverbs
Noun, adverb, adjective, pronoun
Prefix a-
Attribute, subject, predicative, object
Verbs, adjectives
no
Predicate
Verb, noun
Various adverbial midifiers
Predicative, rarely –post-positional attributes
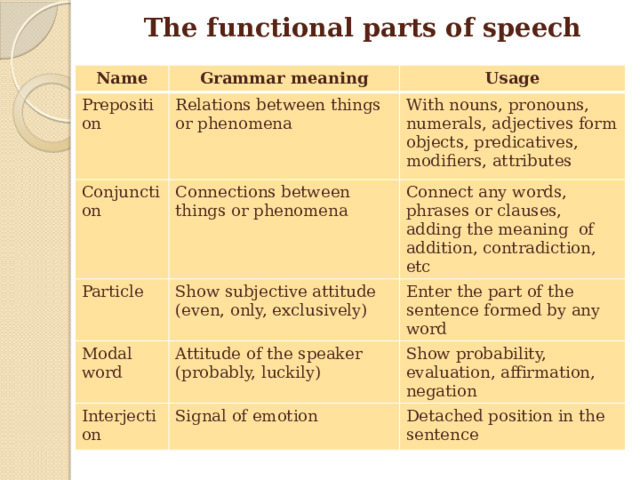
The functional parts of speech
Name
Grammar meaning
Preposition
Usage
Relations between things or phenomena
Conjunction
With nouns, pronouns, numerals, adjectives form objects, predicatives, modifiers, attributes
Connections between things or phenomena
Particle
Modal word
Connect any words, phrases or clauses, adding the meaning of addition, contradiction, etc
Show subjective attitude (even, only, exclusively)
Enter the part of the sentence formed by any word
Attitude of the speaker (probably, luckily)
Interjection
Show probability, evaluation, affirmation, negation
Signal of emotion
Detached position in the sentence

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











 Parts of speech (275.07 KB)
Parts of speech (275.07 KB)
 0
0 1696
1696 9
9 Нравится
0
Нравится
0




