Navbahor district of Navoi region of the Republic of Uzbekistan
33 - secondary school
English teacher Turakulova Nafisa Faxriddinovna
A national flag is a flag that represents and symbolizes a country. The national flag is flown by the government of a country, but can usually also be flown by citizens of the country. A national flag is designed with specific meanings for its colours and symbols. The colours of the national flag may be worn by the people of a nation to show their patriotism, or related paraphernalia that show the symbols or colours of the flag may be used for those purposes.
The design of a national flag may be altered after the occurrence of important historical events. The burning or destruction of a national flag is a greatly symbolic act.
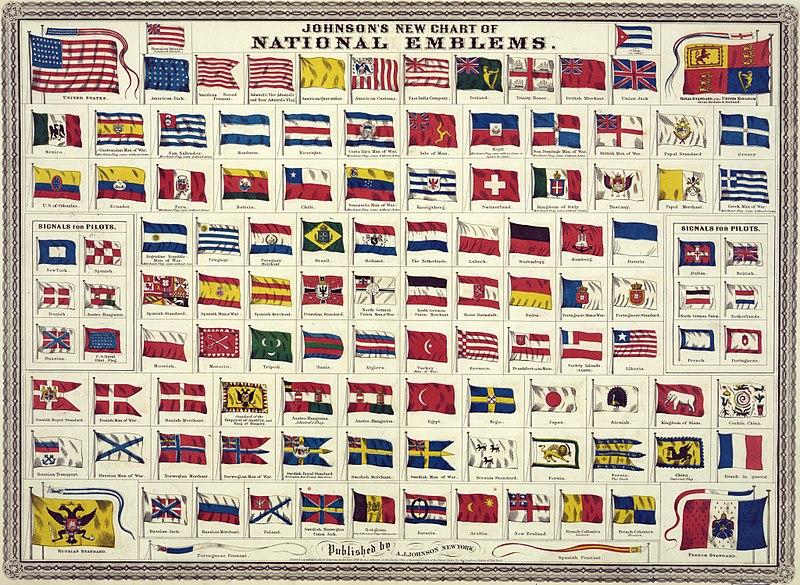
Johnson's new chart of national emblems, published c. 1868. The large flags shown in the corners are the 37-star flag of the United States (flown 1867–1877), the Royal Standard of the United Kingdom, the Russian Imperial Standard, and the French tricolore with inset Imperial Eagle. Various other flags flown by ships are shown. The Flag of Cuba is labelled "Cuban (so called)". The Chinese dragon on the Flag of China was drawn mistakenly as a western dragon.
The national flag is often, but not always, mentioned or described in a country's constitution, but its detailed description may be delegated to a flag law passed by the legislative, or even secondary legislation or in monarchies a decree.
Thus, the national flag is mentioned briefly in the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany of 1949 "the federal flag is black-red-gold" (art. 22.2 Die Bundesflagge ist schwarz-rot-gold), but its proportions were regulated in a document passed by the government in the following year. The Flag of the United States is not defined in the constitution but rather in a separate Flag Resolution passed in 1777.
Minor design changes of national flags are often passed on a legislative or executive level, while substantial changes have constitutional character. The design of the flag of Serbia omitting the communist star of the flag of Yugoslavia was a decision made in the 1992 Serbian constitutional referendum, but the adoption of a coat of arms within the flag was based on a government "recommendation" in 2003, adopted legislatively in 2009 and again subject to a minor design change in 2010. The Flag of the United States underwent numerous changes because the number of stars represents the number of states, proactively defined in a Flag Act of 1818 to the effect that "on the admission of every new state into the Union, one star be added to the union of the flag"; it was changed for the last time in 1960 with the accession of Hawaii.
A change in national flag is often due to a change of regime, especially following a civil war or revolution. In such cases, the military origins of the national flag and its connection to political ideology (form of government, monarchy vs. republic vs. theocracy, etc.) remains visible. In such cases national flags acquire the status of a political symbol.
The flag of Germany, for instance, was a tricolour of black-white-red under the German Empire, inherited from the North German Confederation (1866). The Weimar Republic that followed adopted a black-red-gold tricolour. Nazi Germany went back to black-white-red in 1933, and black-red-gold was reinstituted by the two successor states, West Germany and East Germany, with East Germany's flag being defaced with Communist symbols, following World War II. Similarly the flag of Libya introduced with the creation of the Kingdom of Libya in 1951 was abandoned in 1969 with the coup d'état led by Muammar Gaddafi. It was used again by National Transitional Council and by anti-Gaddafi forces during the Libyan Civil War in 2011 and officially adopted by the Libyan interim Constitutional Declaration.
T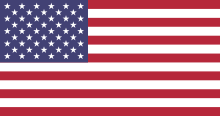 he flag of the United States of America, often referred to as the American flag or U.S. flag, is the national flag of the United States. It consists of thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white, with a blue rectangle in the canton (referred to specifically as the "union") bearing fifty small, white, five-pointed stars arranged in nine offset horizontal rows, where rows of six stars (top and bottom) alternate with rows of five stars. The 50 stars on the flag represent the 50 states of the United States of America, and the 13 stripes represent the thirteen British colonies that declared independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain, and became the first states in the U.S. Nicknames for the flag include the Stars and Stripes, Old Glory, and the Star-Spangled Banner.
he flag of the United States of America, often referred to as the American flag or U.S. flag, is the national flag of the United States. It consists of thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white, with a blue rectangle in the canton (referred to specifically as the "union") bearing fifty small, white, five-pointed stars arranged in nine offset horizontal rows, where rows of six stars (top and bottom) alternate with rows of five stars. The 50 stars on the flag represent the 50 states of the United States of America, and the 13 stripes represent the thirteen British colonies that declared independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain, and became the first states in the U.S. Nicknames for the flag include the Stars and Stripes, Old Glory, and the Star-Spangled Banner.
A national emblem is an emblem or seal that is reserved for use by a nation state or multi-national state as a symbol of that nation. Many nations have a seal or emblem in addition to a national flag and a national coat of arms. Other national symbols, such as national birds, trees, flowers, etc., are listed at lists of national symbols.
national emblem is an emblem or seal that is reserved for use by a nation state or multi-national state as a symbol of that nation. Many nations have a seal or emblem in addition to a national flag and a national coat of arms. Other national symbols, such as national birds, trees, flowers, etc., are listed at lists of national symbols.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











 National flags and emblems - национальные флаги и эмблемы (258.86 KB)
National flags and emblems - национальные флаги и эмблемы (258.86 KB)
 0
0 521
521 1
1 Нравится
0
Нравится
0



