Hello guys,
How are you there? Today we’ having another video on English Grammar. And I’m ready to start.
I’ve got an email from Pall here. He’s writing about his summer plans. Let’s have a look at it.

By the way, do you think summer jobs are a good idea? Why? Why not?
Can you get any summer job in your country?
In this lesson we’re going to look at the most common ways of expressing the future in English:
1. Future Simple
2. Present Simple
3. Present Continuous
4. and the construction to be going to
Look through the email again and find the examples of these forms in it.
1. Future Simple:
I’ll probably spend my morning on the beach with my cousins and then I’ll work with them in the evenings.
… I won’t miss British weather!
I’ll send you a postcard from France!
2. Present Simple
My flight is on the day after we finish school and fly back to the UK on 29 August.
3. Present Continuous
My uncle is starting a new cafe this summer
4. Construction to be going to
What are you going to do in the summer?
I’m going to France.
I’m going to help him and work as a waiter there.
I’m going to miss hanging out with my friends…
Future Simple is formed with the help of will + infinitive.
|
Positive |
He will be a famous designer. They will go swimming tomorrow. |
|
Negative |
He will not (won’t) be a famous designer. They will not ( won’t) go swimming tomorrow. |
|
Question |
Will he be a famous designer? Will they go swimming tomorrow? |
Remember! The verb to be has three forms am/is/are.
|
Positive |
I am going to watch a video on YouTube. He is (‘s) going to buy a new tablet. They are (‘re) going to have a lesson tonight. |
|
Negative |
I’m not going to watch a video on YouTube. He is not (isn’t) going to buy a new tablet. They are not (aren’t) going to have a lesson tonight. |
|
Question |
Am I going to watch a video on YouTube? Is he going to buy a new tablet? Are they going to have a lesson tonight? |
Present Continuous is formed with the help of to be + verb with the ing-suffix.
|
Positive |
I am having an interview at 5 o’clock. She is leaving tomorrow. They are going out tonight. |
|
Negative |
I am not having an interview at 5 o’clock. She is not (isn’t) leaving tomorrow. They are (aren’t) going out tonight. |
|
Question |
Am I having an interview at 5 o’clock. Is she leaving tomorrow? Are they going out tonight? |
Present Simple
We form the Present Simple with the first form of the verb for I/We/You/They. We usually add -s(-es) to the third person singular (He/She/It).
Our train arrives at midnight.
The lessons start at 8 a.m.
In questions and negative sentences, we use do/don’t with I/we/you/they and does/doesn’t with he/she/it.
Our train does not (doesn’t) arrive at midnight.
The lessons do not (don’t) start at 8 a.m.
Does our train arrive at midnight?
Do lessons start at 8 a.m.?
Look at the future forms of can and must.
I can save some money. – I’ll be able to save some money.
I must be back at two. – I’ll have to be back at two.
Now let’s focus on the usage of Future Simple, Present Simple, Present Continuous and be going to.
Listen and say: which of these tenses is used in the following cases?
· for on-the-spot decisions.
For example:
We haven’t got any juice. I’ll go to the corner shop and get some.
The phone is ringing. – Don’t worry. I’ll answer it myself.
· for predictions based on what we think, believe or imagine. Especially with: I expect, I believe, I’m sure, I’m afraid, probably, etc.
For example:
I hope, he will like his birthday present.
Probably, they will stay with us.
I think he will come.
· for actions which we cannot control but which will definitely happen.
Jack will be seventeen next year.
· to make a request.
Will you do me a favour?
Will you lend me ten pounds?
· to promise to do something.
Don’t worry. I’ll fix your bike tomorrow.
I’ll be back at eight, Mum. I promise!
We normally use Future Simple in all these cases.
Which of these is used for?
· predictions based on what we can see or what we know, especially when there is evidence.
For example:
Look! The driver has lost control of the car. He’s going to crash!
That boy is going to climb a tree.
· for intentions, plans or ambitions for the future.
They are going to get married next month. (they have already decided to do it.)
She is going to keep to a diet.
Right you are! We’re talking about the construction be going to.
To talk about fixed arrangements and plans in the near future, we use … Present Continuous.
For example:
I’m playing tennis on Friday.
He’s having dinner with Betty this evening. (It’s a date.)
We are flying to Paris tonight.
And finally,
We use the Present Simple to talk about timetables/ programmes or scheduled events.
For example:
What time does the concert begin?
The next bus goes to the town center.
The train leaves at 8 o’clock in the morning.
Now it’s time to practice the rule.
Charlie: Hi, Bella. Are you OK? You look worried!
Bella: I am. My interview at the bakery is in half an hour!
Charlie: I didn’t know you were looking for a job.
Bella: Yes. I’m going on holiday next month; it’s all booked now, so I need to save some money!
Charlie: Oh, I see. And where are you going?
Bella: Scotland – I can’t wait. My friend’s grandparents have invited us, so we’ll stay at their house in Edinburgh.
Charlie: Cool! Will you be able to travel around Scotland a bit?
Bella: Yes, definitely. We plan to go to Loch Ness and Glasgow.
Charlie: I hope you’ll have a great time – and good luck with the interview!
Bella: Thanks.
Well guys, we’ve finished with the most common ways of expressing future actions. Join us at our grammar lessons at videouroki.net and you’ll realize that grammar can be easy and enjoyable!

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход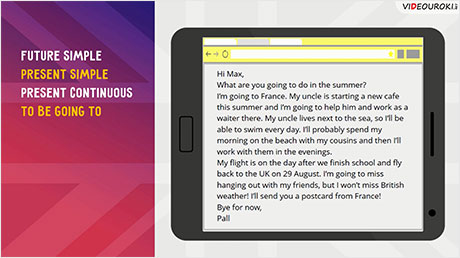



 1019
1019

