Tom (Allan’s brother): The weather is awful. It’s going to rain!
Allan: That’s excellent news!
Tom: Erm…why?
Allan: Because I promised to help Dad in the garden and I don’t want to now. I don’t think we’ll go out in the rain! (smiling)
I’m going to lie on the sofa and watch a DVD instead!
Tom: Good idea! I’ll join you!
Later…
Dad: Allan! Tommy! I have to go now. I’m meeting your granny at the station. Her train comes at 5 o’clock. Can you please finish tidying the garage for me?
So, look at the highlighted forms in the dialogue.
Will go, will join are the Future Simple forms,
am/is going to is the construction to be going to,
am meeting is the Present Continuous form
and comes is in the Present Simple Tense
What do you think all these forms are used in the dialogue for?

In this lesson we’re going to look at the most common ways of expressing the future in English:
1. Future Simple
2. Present Simple
3. Present Continuous
4. and the construction to be going to
We’ll revise their formation and you’ll get to know in what situations to use them.
So, let’s get started.
First, let’ s revise the formation of the Present Simple/Present Continuous/Future Simple and the construction to be going to.
Complete the tables.
Future Simple
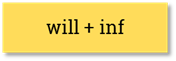
|
Positive |
He will be a famous singer. They will have a party tomorrow. |
|
Negative |
He will not (won’t) be a famous singer. They will not ( won’t) have a party tomorrow. |
|
Question |
Will he be a famous singer? Will they have a party tomorrow? |
Remember! The verb to be has three forms am/is/are.
|
Positive |
I am going to watch a DVD. He/She/It is (‘s) going to buy a new laptop. We/You/They are (‘re) going to the cinema tonight. |
|
Negative |
I am not going to watch a DVD. He is not (isn’t) going to buy a new laptop. We are not (aren’t) going to the cinema tonight. |
|
Question |
Am I going to watch a DVD? Is he going to give her some money? Are we going to the cinema tonight? |
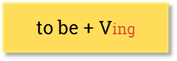
|
Positive |
I am meeting granny at 5 o’clock. She is leaving tomorrow. They are going out tonight. |
|
Negative |
I am not meeting granny at 5 o’clock. She is not (isn’t) leaving tomorrow. They are (aren’t) going out tonight. |
|
Question |
Am I meeting granny at 5 o’clock? Is she leaving tomorrow? Are they going out tonight? |
Present Simple
We form the Present Simple with the first form of the verb for I/We/You/They. We usually add -s(-es) to the third person singular (He/She/It).
Our bus leaves at 11.00.
The doors open at 8 am.
In questions and negative sentences, we use do/don’t with I/we/you/they and does/doesn’t with he/she/it.
Our bus does not (doesn’t) leave at 11.00.
The doors do not (don’t) open at 8 am.
Does our bus leave at 11.00?
Do the doors open at 8 am?
Future Simple is used for:
· on-the-spot decisions.
For example:
We haven’t got any juice. I’ll go to the corner shop and get some.
The phone is ringing. – Don’t worry. I’ll answer it myself.
· for predictions based on what we think, believe or imagine. Especially with: I expect, I believe, I’m sure, I’m afraid, probably, etc.
For example:
I hope, he will like his birthday present.
Probably, they will stay with us.
I think he will come.
· for actions which we cannot control but which will definitely happen.
Jack will be seventeen next year.
· to make a request.
Will you do me a favour?
Will you lend me ten pounds?
· to promise to do something.
Don’t worry. I’ll fix your bike tomorrow.
I’ll be back at eight, Mum. I promise!
Be going to is used for:
· predictions based on what we can see or what we know, especially when there is evidence.
For example:
Look! The driver has lost control of the car. He’s going to crash!
That boy is going to climb a tree.
· for intentions, plans or ambitions for the future.
They are going to get married next month. (they have already decided to do it.)
She is going to keep to a diet.
We use the Present Continuous:
· to talk about fixed arrangements and plans in the near future.
For example:
I’m playing tennis on Friday.
He’s having dinner with Betty this evening. (It’s a date.)
We are flying to Paris tonight.
Present Simple
· We use the present simple to talk about timetables/ programmes or scheduled events.
For example:
What time does the concert begin?
The next bus goes to the town center.
The train leaves at 8 o’clock in the morning.
Now it’s time to practice the rule.
Identify the tenses, then match them with the correct description.
Check your guesses.
1. Will you give me your phone?
E. polite request
2. I’m sure you’ll have a wonderful holiday.
B. I think this will happen
3. The bus to Cambridge departs in an hour.
G. timetable/programme
4. They are delivering the parcel tomorrow.
A. fixed arrangement in the near future
5. Look at the baby! It’s going to eat that worm!
F. prediction based on what I see
6. I’m hungry. I’ll make a sandwich.
D. on-the-spot decision
7. He’s going to take a few days off next week.
C. intention to do something
Harry: Well guys, we’ve finished with the most common ways of expressing future actions. Sorry, but I have to hurry up now. I’m going to help Allan tidy the garage.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход



 1079
1079



