You plan vacations to faraway lands. What about Mars? Won't it be exciting? Although it sounds unbelievable, it may turn into a reality. Thanks to space exploration, we might be able to find a planet where life can exist.

But these are only possibilities. Let's discuss the pros and cons of exploring space.
Pros
Space research introduced developments in science and opened doors to new information.
Satellites help locate minerals and fossil fuels.
Satellites help us in forecasting weather and in predicting natural calamities.
Satellite communication, TV, radio, and GPS are among the other advantages of space exploration.
We have been able to harness solar energy due to our knowledge of the sun. Through space exploration, we may be able to find new energy sources.
Satellites help the scientists study the changes in the environment, like global warming and ozone depletion.
Space exploration has helped answer questions like how the Earth was formed or where organic materials come from.
By exploring space, scientists can now know when an asteroid is going to pass close to the Earth or whether there are chances of it striking our planet and the damage it may cause.
Space research needs the use of high-end technology, including specialized communication devices, small computers, robots, and other space equipment. Thus Space exploration drives innovation.
Space exploration programs can help achieve cooperation between countries. They share expenses and the research costs do not burden just one country.
Cons
One of the most important cons of space exploration is the money spent on research.
Critics of space exploration argue that it is not right to spend money on something like space research when several people on the planet are unable to meet even their basic needs.
Space exploration risks human life. The stay in a spacecraft is not easy. Effects of radiation on the body, muscle and bone loss resulting from microgravity are some of the health risks during space travel.
We always associate space research with the discovery of life. But exploring space may land us in trouble. We may discover something that is harmful to the living beings on our planet. There is a possibility of finding dangerous organisms.
What we leave behind in space, known as space junk or space debris, leads to space pollution. The debris include coolant droplets, dust, non-functional spacecraft, old satellites, and pieces of any man-made objects that continue to orbit the Earth.

Uniting the world may be cited as an advantage of space exploration. However, it may lead to disputes within nations. Satellites could be used by one country to spy over another.
Humans have always looked at the heavens and wondered about the nature of the objects seen in the night sky. With the development of rockets and the advances in electronics and other technologies in the 20th century, it became possible to send machines and animals and then people above Earth’s atmosphere into outer space.
However, there’s still so much about space we just don’t know about yet.
But how did space travel and exploration boom begin?
Early Discoveries
2773 BC
The Egyptians develop a 365-day calendar. It’s based on the many stages or phases of the star Sirius.
AD 1543
Nicolaus Copernicus, an astronomer, says Earth is not the center of the universe.
The sun is.
1609
Galileo Galilei creates his own telescope. He is able to look at the moon, discover four moons of Jupiter and see a supernova.
1687
Sir Isaak Newton creates his Newton’s Laws. They are the three laws of motion for Earth, the other planets and the moon.
After the World War II the United States and the Soviet Union wanted to display their powers by reaching for the stars. Both powers were able to reach a success.
In 1942 the German V2 was the first rocket to reach 100km from the Earth’s surface. The rocket was designed by Werner Von Braun.

During the final days of World War II this technology was obtained by both the Americans and Soviets as were its designers.
In 1947, the first animals were sent into space. Fruit flies were used to study the effects of space travel on animals, and were chosen because they are more similar to humans than you might imagine!
The flies travelled with a supply of corn to eat on the flight.
Albert II, was the first monkey in space. He was a Rhesus monkey, a type of monkey that originally comes from Asia.
Albert went into space on 14th June, 1949 in a specially adapted American V2 rocket, that flew to a height of 83 miles from earth.
On 4th October 1957, Russia launched the first satellite into space – Sputnik 1. Sputnik was the first satellite in orbit around the earth. Today there are over 500 working satellites in space.
In November 1957, the Russian space dog Laika became the first animal to orbit the earth. Laika travelled in a spacecraft known as Sputnik 2 and her mission helped scientists understand whether people could survive in space.
On 12th April 1961, Russian Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first man in space. Gagarin's spacecraft, Vostok 1, completed one orbit of the earth, and landed about two hours after launch. Gagarin had to land using his parachute, because the Vostok 1 was designed to crash land!
The first woman in space was Russian cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova. After her 1963 mission, Valentina became an important member of the Russian Government, and has been awarded many honours and prizes for her achievements. A crater on the far side of the Moon is named after her!
A. A. Leonov achieved the first "spacewalk" in 1965.
Russian probe Luna 9 landed successfully on the Moon in 1966.
Lunokhod 1 was the first remote-controlled robot landed on another world in 1970 by the Soviet Union.
In the early 1960s the United States organized the Apollo space program. This research program concentrated on landing a man on the moon.
Neil Armstrong walked on the lunar surface in July 1969.
From 1971 American astronauts on the fourth, fifth and sixth Apollo missions used a moon car to explore the moon. Known as the Lunar Rover, it was electric powered.
Not just satisfied with the Moon both of the super powers wanted to explore the rest of the Solar system. Unmanned probes were sent to visit the Solar system, to other planets and moons. Voyages to Venus and Mars were made by the Soviet spaceships, voyages to Uranus, Jupiter, Neptune and Saturn – by the American spaceships.
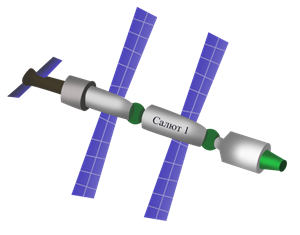
Meanwhile on 19 April 1971 the Russians launched the first space station, Salyut I. On 14 May 1973 the USA launched a space station named Skylab.
Until 12th April 1981 all spacecraft were designed to be used only once. The Space Shuttle, was designed to be reused for up to 100 visits to space, in an attempt to make space travel less expensive.
On January 28th 1986, tragedy struck. Space Shuttle Challenger exploded shortly after launch, because of a fuel system failure. All seven astronauts on board were killed, and all shuttles were grounded for nearly three years.
Then in February 1986 the Russians launched their Mir space station. In 1988 Vladimir Titov and Musa Manarov became the first human beings to spend a year in space. Mir fell back to Earth in 2001.

On that same year The International Space Station (ISS) - a huge space station for research and space exploration began construction, with the final major module arriving in 2010.
In 2000 the first permanent crew moved into the International Space Station (ISS), where crews of astronauts have been living ever since.
On the 28th April 2001 American millionaire Dennis Tito became the first space tourist when he paid around 20 million dollars for a ride in a Russian Soyuz spacecraft. Dennis spent a week in orbit, most of the time visiting the International Space Station. He had to train for 900 hours just to be a passenger!
To sum up what you’ve learnt at the lesson, match the dates and events of space exploration.
1957 – Russia launched the first satellite into space – Sputnik.
1961 – Russian Cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first man in space.
1969 – Neil Armstrong walked on the lunar surface.
1970 – Lunokhod 1 was the first remote-controlled robot landed on another world.
1986 – Mir space station was launched.
2000 – The first permanent crew moved into the International Space Station (ISS).
2001 – American millionaire Dennis Tito became the first space tourist.
You see that the sky is no longer the limit.
Maybe in some years the space travel will become a usual trip.
Do you think space travel would be a positive or negative development?

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход


 0
0 1615
1615


