
Ecosystem
Completed by Alisa Klochkova

What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact.
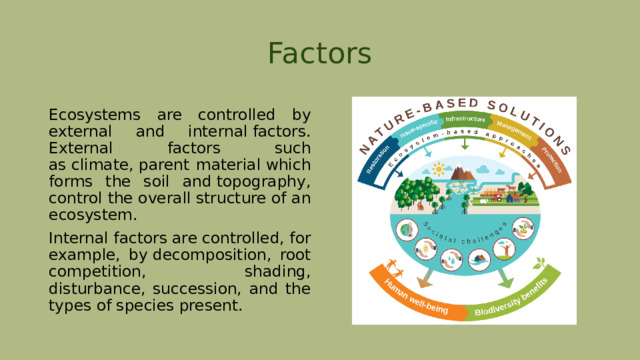
Factors
Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem.
Internal factors are controlled, for example, by decomposition, root competition, shading, disturbance, succession, and the types of species present.
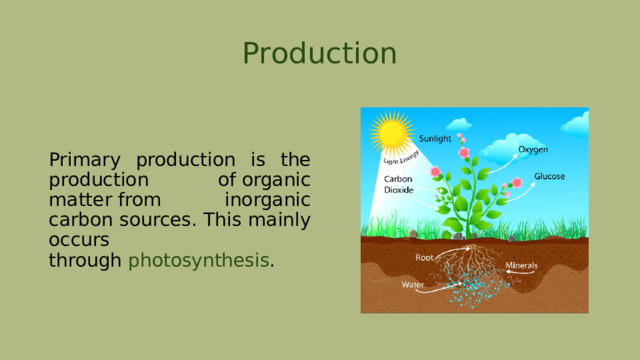
Production
Primary production is the production of organic matter from inorganic carbon sources. This mainly occurs through photosynthesis .
Decomposition
Decomposition processes can be separated into three categories—leaching, fragmentation and chemical alteration of dead material. As water moves through dead organic matter, it dissolves and carries with it the water-soluble components. These are then taken up by organisms in the soil, react with mineral soil, or are transported beyond the confines of the ecosystem.

Dynamics and resilience
Ecosystems are dynamic entities. They are subject to periodic disturbances and are always in the process of recovering from past disturbances.
Disturbance also plays an important role in ecological processes. F. Stuart Chapin and coauthors define disturbance as "a relatively discrete event in time that removes plant biomass".
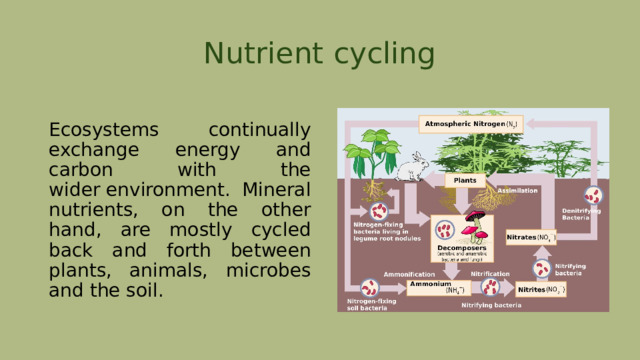
Nutrient cycling
Ecosystems continually exchange energy and carbon with the wider environment. Mineral nutrients, on the other hand, are mostly cycled back and forth between plants, animals, microbes and the soil.
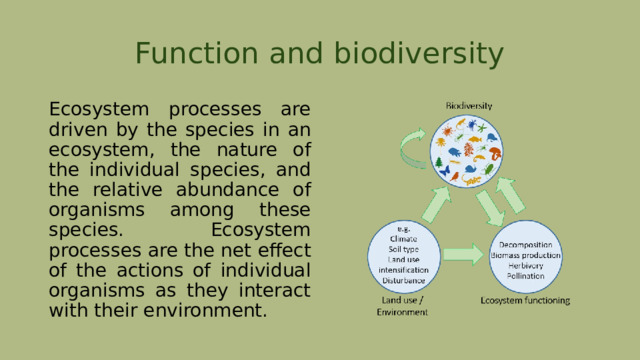
Function and biodiversity
Ecosystem processes are driven by the species in an ecosystem, the nature of the individual species, and the relative abundance of organisms among these species. Ecosystem processes are the net effect of the actions of individual organisms as they interact with their environment.
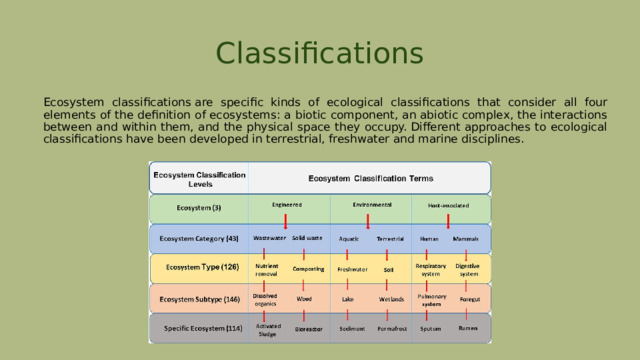
Classifications
Ecosystem classifications are specific kinds of ecological classifications that consider all four elements of the definition of ecosystems: a biotic component, an abiotic complex, the interactions between and within them, and the physical space they occupy. Different approaches to ecological classifications have been developed in terrestrial, freshwater and marine disciplines.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











 Project: Ecosystems (1.74 MB)
Project: Ecosystems (1.74 MB)
 0
0 577
577 9
9 Нравится
0
Нравится
0


