
Early History of Britain

Pre-Roman Period
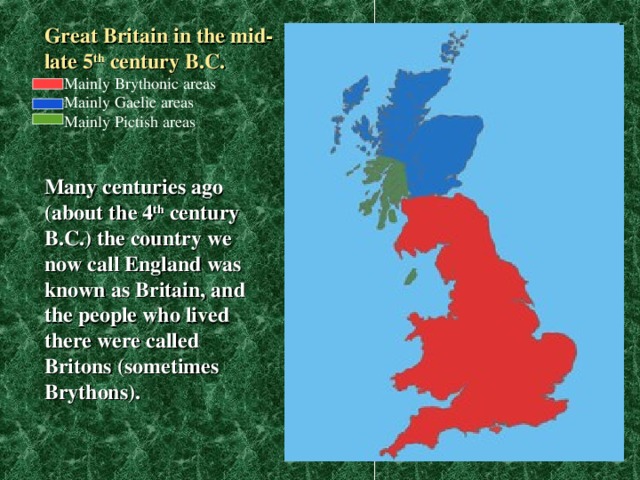
Great Britain in the mid-late 5 th century B.C.
Mainly Brythonic areas
Mainly Gaelic areas
Mainly Pictish areas
Many centuries ago (about the 4 th century B.C.) the country we now call England was known as Britain, and the people who lived there were called Britons (sometimes Brythons).

They were the Celtic people living in Great Britain from the Iron Age through the Early Middle Ages. They spoke the Celtic language known as British or Brythonic.

That primitive society had a warrior class. They did the actual fighting , the free poor served as chariot drivers. Part of a warrior’s ritual was to boast of his victories, and fighting between warriors was an important part of life.

Bronze Age Britons practised the art of mummification at the same time as the Egyptians. Archaeologists unearthed the skeletons of a man, a woman, and a 3-year-old girl under the floor of a prehistoric house at Cladh Hallan on the Scottish island of South Uist.

A mysterious race of ancient Britons who had much in common with people today but belonged to another human species lived in Norfolk almost a million years ago, scientists believe them to be the oldest known human settlers in northern Europe.

Ancient Britons were ruled by a class of priests called Druids. These were members of the ancient Celtic priesthood before the Christian religion.

Jersey copper token depicting a priest. Currencies of the Anglo-Norman Isles, 1813
They were keepers of all the religious teachings, the tribal history and other knowledge important in Celtic society

This Briton Druid Copper Necklace dating back from the 1st to 4th century AD.
This type of necklace was a device that had been used to alter a Druid's voice
They worshipped Gods & Goddesses living in water, stones, trees etc.
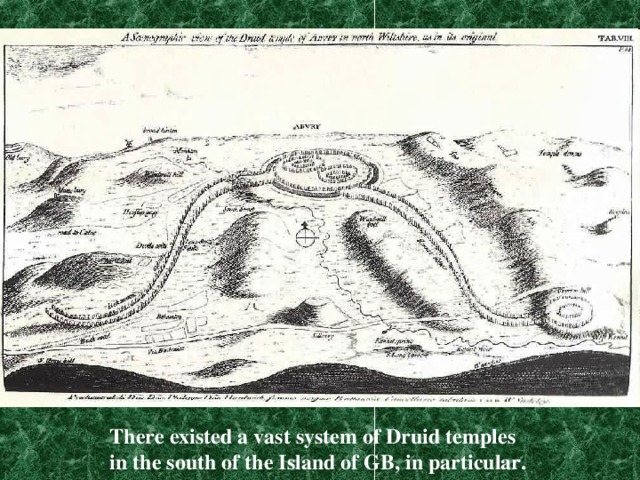
There existed a vast system of Druid temples in the south of the Island of GB, in particular.

Stonehenge, the most famous prehistoric, mysterious circle of upright stones in southern England, is probably, one of the most famous sites in the world. Stonehenge “supported stones” is located in the English county of Wiltshire. It was generally concluded that Stonehenge was constructed as a temple to the sun.

Construction on the great monument began 5,000 years ago; the famous stones that still stand today were put in place about 4,000 years ago.

It is at the centre of the most dense complex of Neolithic and Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred burial mounds.

Scientists are still amazed at extraordinary mathematical sophistication and engineering abilities that the native British developed.

Picture of Stonehenge of 1700
Stonehenge constructors must have had precise astronomical knowledge of the path of the sun risings at dawn on midsummer's morning.

17 th century depiction of Stonehenge
Recent studies have focused on the stone rings as astronomical observatories. The monument must have been deliberately oriented and planned so that on midsummer's morning the sun rose directly over the Heel Stone and the first rays shone into the centre of the monument.

Image of Stonehenge showing the circular layout
A lot of scientists also agree on their possible “magico-religious” uses.

John Constable, Stonehenge, 1836. (Victoria and Albert Museum, London, UK)
The mystery still surrounds its original purpose. In the 12 th century Geoffrey of Monmouth included a fanciful story in his work Historia Regum Britanniae that attributed the monument's construction to Merlin, the magician of the times of King Arthur.
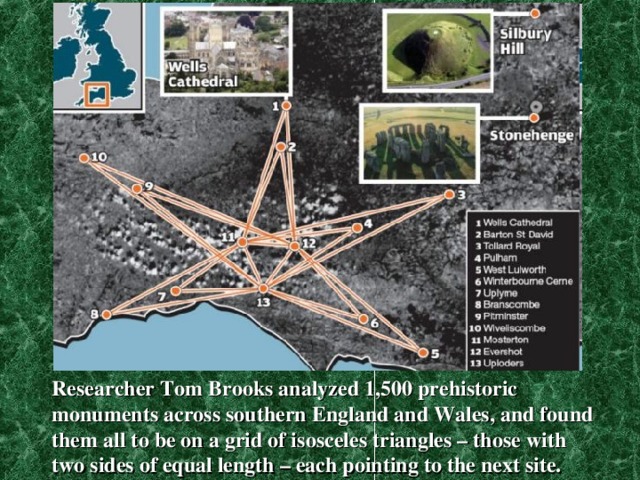
Researcher Tom Brooks analyzed 1,500 prehistoric monuments across southern England and Wales, and found them all to be on a grid of isosceles triangles – those with two sides of equal length – each pointing to the next site.

Silbury Hill near Avebury, Wiltshire
Ancient Britons were able to travel hundreds of miles with remarkable accuracy using landmarks such as Stonehenge .

Stanton Drew "The Cove". Situated in the garden of "The Druids Arms"
Stone markers on hilltops and natural waypoints let them orient, as if they had satellite navigation maps.

A Britons village, drawn by a modern artist
The Britons lived in villages of round houses from wood and mud with thatched roofs. There was a strict differentiation between peasants and warriors in their occupations and social position. There were lots of different tribes ruled by kings or chiefs. Chiefs often fought one another.

A Celtic shield, found in the River Thames (London)
Here is a genuine Celtic warrior shield, found in the River Thames (London). It's too fine for use in battle. Perhaps it was thrown in the river as a gift to the gods.


 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход




































 Презентация по английскому языку "Early History of Britain" (24.76 MB)
Презентация по английскому языку "Early History of Britain" (24.76 MB)
 0
0 1212
1212 106
106 Нравится
0
Нравится
0


