Now the majority of modern video cards are built with either AMD
A video card (also called a display card, graphics card, display adapter or graphics adapter) is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a display (such as a computer monitor). Frequently, these are advertised as discrete or dedicated graphics cards, emphasizing the distinction between these and integrated graphics. At the core of both is the graphics processing unit (GPU), which is the main part that does the actual computations, but should not be confused as the video card as a whole, although "GPU" is often used to refer to video cards.
Most video cards are not limited to simple display output. Their integrated graphics processor can perform additional processing, removing this task from the central processor of the computer.For example, Nvidia and AMD (AT i) produced cards render the graphics pipeline OpenGL and DirectX on the hardware level. In the later 2010s, there has also been a tendency to use the computing capabilities of the graphics processor to solve non-graphic tasks.
Usually the graphics card is made in the form of a printed circuit board (expansion board) and inserted into an expansion slot, universal or specialized (AGP, PCI Express). Some have been made using dedicated enclosures, which are connected to the computer via a docking station or a cable.
Аs MDA, CGA, HGC, Tandy, PGC, EGA, VGA, MCGA, 8514 or XGA were introduced from 1982 to 1990 and supported by a variety of hardware manufacturers.
3dfx Interactive was one of the first companies to develop a GPU with 3D acceleration (with the Voodoo series) and the first to develop a graphical chipset dedicated to 3D, but without 2D support (which therefore required the presence of a 2D card to work). Now the majority of modern video cards are built with either AMD-sourced or Nvidia-sourced graphics chips.] Until 2000, 3dfx Interactive was also an important, and often groundbreaking, manufacturer. Most video cards offer various functions such as accelerated rendering of 3D scenes and 2D graphics, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors (multi-monitor). Video cards also have sound card capabilities to output sound – along with the video for connected TVs or monitors with integrated speakers.
Within the industry, video cards are sometimes called graphics add-in-boards, abbreviated as AIBs, with the word "graphics" usually omitted.
Dedicated vs integrated graphics
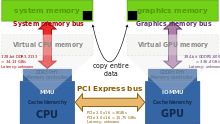
Classical desktop computer architecture with a distinct graphics card over PCI Express. Typical bandwidths for given memory technologies, missing are the memory latency. Zero-copy between GPU and CPU is not possible, since both have their distinct physical memories. Data must be copied from one to the other to be shared.
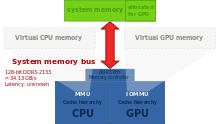
Integrated graphics with partitioned main memory: a part of the system memory is allocated to the GPU exclusively. Zero-copy is not possible, data has to be copied, over the system memory bus, from one partition to the other.
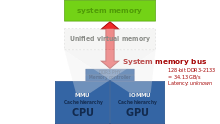
As an alternative to the use of a video card, video hardware can be integrated into the motherboard, CPU, or a system-on-chip. Both approaches can be called integrated graphics. Motherboard-based implementations are sometimes called "on-board video". Almost all desktop computer motherboards with integrated graphics allow the disabling of the integrated graphics chip in BIOS, and have a PCI, or PCI Express (PCI-E) slot for adding a higher-performance graphics card in place of the integrated graphics. The ability to disable the integrated graphics sometimes also allows the continued use of a motherboard on which the on-board video has failed. Sometimes both the integrated graphics and a dedicated graphics card can be used simultaneously to feed separate displays. The main advantages of integrated graphics include cost, compactness, simplicity and low energy consumption. The performance disadvantage of integrated graphics arises because the graphics processor shares system resources with the CPU. A dedicated graphics card has its own random access memory (RAM), its own cooling system, and dedicated power regulators, with all components designed specifically for processing video images. Upgrading to a dedicated graphics card offloads work from the CPU and system RAM, so not only will graphics processing be faster, but the computer's overall performance may also improve.
Both AMD and Intel have introduced CPUs and motherboard chipsets which support the integration of a GPU into the same die as the CPU. AMD markets CPUs with integrated graphics under the trademark Accelerated Processing Unit (APU), while Intel markets similar technology under the "Intel HD Graphics and Iris" brands. With the 8th Generation Processors, Intel announced the Intel UHD series of Integrated Graphics for better support of 4K Displays. Although they are still not equivalent to the performance of discrete solutions, Intel's HD Graphics platform provides performance approaching discrete mid-range graphics, and AMD APU technology has been adopted by both the PlayStation 4 and Xbox One video game consoles.
As the processing power of video cards has increased, so has their demand for electrical power. Current high-performance video cards tend to consume a great deal of power. For example, the thermal design power (TDP) for the Ge Force GTX TITAN is 250 Watts. While CPU and power supply makers have recently moved toward higher efficiency, power demands of GPUs have continued to rise, so video cards may have the largest power consumption in a computer. Although power supplies are increasing their power too, the bottleneck is due to the PCI-Express connection, which is limited to supplying 75 Watts Modern video cards with a power consumption of over 75 Watts usually include a combination of six-pin (75 W) or eight-pin (150 W) sockets that connect directly to the power supply. Providing adequate cooling becomes a challenge in such computers. Computers with multiple video cards may need power supplies in the 1000–1500 W range. Heat extraction becomes a major design consideration for computers with two or more high-end video cards.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











 Now the majority of modern video cards are built with either AMD (52.07 KB)
Now the majority of modern video cards are built with either AMD (52.07 KB)
 0
0 162
162 0
0 Нравится
0
Нравится
0


