
CTD FORMAT Drug master file
Drug Master File
- A Drug Master File (DMF) is a submission to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that may be used to provide confidential detailed information about facilities, processes, or articles used in the manufacturing, processing, packaging, and storing of one or more human drugs.
- Beginning on May 5, 2018, new DMFs other than Type III DMFs, as well as all documents submitted to existing DMFs other than Type III DMFs, must be submitted using the Electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD). DMF submissions that are not submitted in eCTD format after this date will be rejected. For Type III DMFs, the requirement goes into effect on May 5, 2020.

TYPES OF DMFs
The types of DMFs are:
- Type I Manufacturing Site, Facilities, Operating Procedures, and Personnel (no longer applicable)
- Type II Drug Substance, Drug Substance Intermediate, and Material Used in Their Preparation, or Drug Product
- Type III Packaging Material
- Type IV Excipient, Colorant, Flavor, Essence, or Material Used in Their Preparation
- Type V FDA Accepted Reference Information
The recommendations in the DMF Guidance are, in general, still applicable. However the information below provides additional information or clarification of the recommendations in the Guidance. This information provided below falls into four categories:
- Category 1: Recommendations which are no longer applicable due to changes in regulations or guidances. Category 2: Additional clarification of recommendations in the Guidance. Category 3: New information for aspects of DMF filing that was not in effect when the Guidance was written. Category 4: Information related to the Generics Drug User Fee Act (GDUFA)

Common Technical Document
The Common Technical Document ( CTD ) is a set of specification for application dossier for the registration of Medicines and designed to be used across Europe, Japan and the United States. It is an internationally agreed format for the preparation of applications regarding new drugs intended to be submitted to regional regulatory authorities in participating countries. It was developed by the European Medicines Agency (EMA, Europe), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA, US) and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (Japan). The CTD is maintained by the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH)

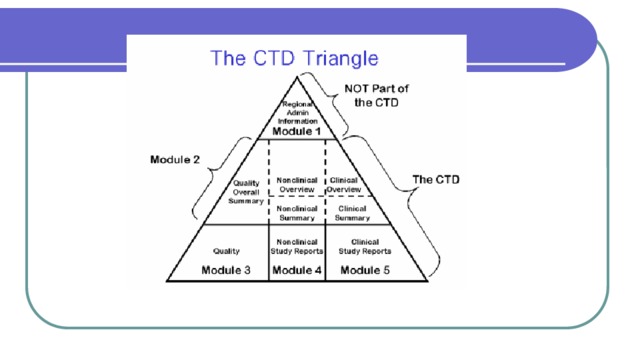
The Common Technical Document is divided into five modules:
- Administrative and prescribing information
- Overview and summary of modules 3 to 5
- Quality (pharmaceutical documentation)
- Preclinical (Pharmacology/Toxicology)
- Clinical – efficacy and safety (Clinical Trials)

The main objective of the development of CTD is to harmonize the requirements for the submission of registration documents, which allows them to be sent to the registration and licensing authorities of different countries as a single dossier (for registration of drugs).
Expert working groups (EWGs) on quality, safety and efficacy control of medicines have been established to prepare the regulatory documents of CTD ICH. The last working meetings were held in San Diego (USA) — in November 2000, in Tokyo (Japan) - in may 2001 and as part of the so-called ICH Steering Committee (ICH steering Committee), in Brussels (Belgium) - in February 2002.

CTD, initially applicable exclusively to new chemical compounds and biotechnological preparations (as specified in sections Q6A and Q6B ICH), has since been used also for other groups of preparations and all types of trade licenses (for original preparations, generics, CTC preparations). In the future, OCD may be used in clinical trials.The use of CTD for planning the development of the pharmaceutical industry is promising, it can also be used by experts in the preparation of appropriate reviews for all types of applications for registration of drugs.There are some differences in the implementation of the TSA in the countries that have acceded to the ICH agreement.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











 Drug master file (126.21 KB)
Drug master file (126.21 KB)
 0
0 471
471 0
0 Нравится
0
Нравится
0


