
DENSITY
- Depends on:
- Mass Volume
- Mass Volume
- Mass
- Volume
D = m/v (g/cm 3 )
Mass usually expressed in grams
Volume usually expressed in cm 3 or liters, etc.
- D = m/v (g/cm 3 ) Mass usually expressed in grams Volume usually expressed in cm 3 or liters, etc.
- D = m/v (g/cm 3 ) Mass usually expressed in grams Volume usually expressed in cm 3 or liters, etc.

What would take up more space??? A kilogram of feathers….. or a kilogram of steel??
ROCKS - pass around
OR

Density is the measure of the “compactness” of a material
- The proximity of like atoms or molecules
- More than just the “heaviness” of a substance, density includes how much space an object takes up!!
- All substances have density including liquids, solids, and gases
Bread slice and compacted bread in large flask of water
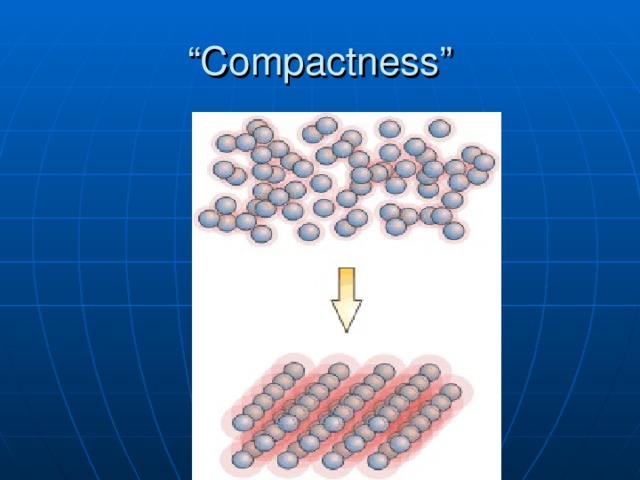
“ Compactness”
Hot air balloon - Describe how a hot air balloon works. Defend your argument.

Gases
- How much kinetic energy do the molecules have??
- The greater the kinetic energy
- …… the greater the volume
- …… and the less dense that gas is!!
- Therefore, cold air is more dense than warm air

Gases
- Real life application…..
- Low pressure weather system means warmer air tends to rise,
- High pressure systems indicate a colder more dense air mass that will…….
- SINK!!!

Balloon and liquid nitrogen
- http: //hyperphysics . phy-astr . gsu . edu/hbase/thermo/balloon .html#c1
- http://paer.rutgers.edu/pt3/movies/TVrhoandFb.mov
What happens to the gasses in the balloon when it is placed in liquid nitrogen? (nitrogen condensed to -196 degrees celcius)
www.dkimages.com

LIQUIDS
- The more dissolved solids in a solution, the more dense (such as ocean water)
- Cold water in lakes tend to sink (this creates a constant mixing of water, nutrients, and other substances)
- Kinetic energy again!!
- Kinetic energy again!!
- Kinetic energy again!!
- Kinetic energy again!!
Straw solute
Denser layers to less dense layers…..

What would happen????
- Mercury density = 13600kg/m 3
- Lead density = 11340kg/m 3
Sinking vial - make it float

Lead floats on liquid mercury!

Solids
Ice vs. water…..

SOLIDS
- Ice is less dense than water (which is why lakes and ponds have a thin layer of ice covering in winter, with water underneath)
- Various rocks, woods, metals have a characteristic density specific to that substance
Beans/ping pong ball; Big jug of water in a pool
Wouldn’t you like to have a bunch of THIS dense material?

Archimedes and the Kings Crown
250 b.c., the Greek mathematician Archimedes - story
Factors affecting Density
- Temperature
- Pressure
Add several drops of red food color to each of two 250-mL Erlenmeyer flasks; fill them with warm tap water. (If tap water is not warm, heat some tap water on a hot plate to 40-45 °C.)
Add several drops of blue food coloring to each of the other two 250-mL Erlenmeyer flasks; fill them with cool tap water.
Predict the outcome when one flask is inverted over the other.
Place a paper card on top of the vessel filled with warm water. Invert the flask making sure to hold the card in place. Stack it on top of one of the cool water flasks. Remove the card. Remain prepared to catch the flasks.
** Visual here.
Place a paper card on top of the flask filled with cool water. Invert the flask making sure to hold the card in place. Stack it on top of the other warm water flask. Remove the card.
** Visual here.
Wide mouth containers may also be used.

Factors affecting Density
- Dissolved solids – in liquids
- Concentration and kind of substances
- Concentration and kind of substances
- Concentration and kind of substances

FACTORS AFFECTING DENSITY
- ATomS!!!!

Relative Density
- The density of a material or substance, relative to another substance
- Expressed in a ratio: water = 1g/cc
- Water is the substance to which we generally compare other substances
- ALSO known as SPECIFIC GRAVITY
Relative Liquid densities : Oil, colored water, and corn syrup in a graduated cylinder.
An H2O ice cube floats in liquid H2O but floats in rubbing alcohol. A can of diet coke floats in water while a can of regular coke sinks (can determine density of sugar versus NutraSweet using balance).

- How are Submarines like fish….
- The swim bladder in bony fish control their relative density in order to rise or dive in the water….buoyancy
- When air is added to the swim bladder, by diffusion through the blood vessels in the bladder walls, the fish becomes less dense overall
- when air is removed fish become more dense
- By changing the volume of air in the bladder, the fish’s density can be made equal to that of the surrounding water at a given depth.
Air bladder when pulled up to quickly

Absolute DENSITY
- The density of a material in its closest “packed form”
- For water: Absolute Density = 1000kg/m 3
at 4 0 C and 1 atm(pressure)
in other words, the greatest density of water is at 4 0 C
- at 4 0 C and 1 atm(pressure) in other words, the greatest density of water is at 4 0 C

DETERMINING DENSITY
- Regular Shapes – mass, then determine the volume by formula
EX: cubes, cylinders, spheres, cones, etc.
- Irregular shapes – mass, then measure displacement of a liquid (usually water) by that irregularly shaped object

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











 Density-is a characteristic property of matter. (2.17 MB)
Density-is a characteristic property of matter. (2.17 MB)
 0
0 482
482 4
4 Нравится
0
Нравится
0









