BASIC STRUCTURE OF COMPUTER
All types of computers follow a same basic logical structure and perform the following five basic operations for converting raw input data into information useful to their users.
Following diagram shows the basic structure of Computer:
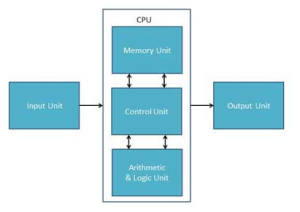
This unit contains devices with the help of which we enter data into computer. This unit makes link between user and computer. The input devices translate the information into the form understandable by computer.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU is considered as the brain of the computer. CPU performs all types of data processing operations. It stores data, intermediate results and instructions(program). It controls the operation of all parts of computer.
CPU itself has following three components
ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
Memory Unit
Control Unit
Output Unit
Output unit consists of devices with the help of which we get the information from computer. This unit is a link between computer and users. Output devices translate the computer’s output into the form understandable by users.
The CPU is can be expanded into three main parts: The ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit), The Bus interface Unit, and The Control Bus. The clock is an electronic circuit that gives regular pulses to the CPU. Faster clock speeds means more pulses to the CPU and the instructions are stepped through faster. The memory chip contains millions of separate memory stores and each of these locations has a unique number. This is known as memory address. The CPU stores data at any of these addresses and fetch the content back when required.
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. These chips store the instructions for running the operating system and any computer application. This memory also stores all the data that is being worked on. RAM is a volatile memory which means that it only stores data while the computer remains switched on. When switched off, it loses all the stored data. ROM (Read Only Memory) on the other hand is a chip with program instructions permanently burned into it. The content is not lost even if the machine is switched off.
The CPU can either fetch data from or write data when the appropriate memory location is accessed. Such data is transferred from the CPU to the memory location along the Data Bus. The control Bus is a set of tracks on the computer’s motherboard that run from the CPU to the devices and works under the direction of the CPU.
Humans speak to one another in a particular language and we use different words and letters. Although we type words and letters in the computer, the computer translates those words and letters into numbers. Computers talk and understand in numbers. Those number systems are: Decimal, Hexadecimal, and Binary.
The Decimal Number System is the system is most frequently used in arithmetic and in everyday life. The decimal number system is also known as the base 10 number system as the position in the number represents an incremental number with a base of 10. Each position only contains a number between 0 and 9.
The Hexadecimal number system is used to represent memory addresses or colours. It is also known as the base 16 number system, because each position in the number represents an incremental number with a base of 16. Since the number system is represented in 16s, there are only 10 numbers and 5 letters (A to F).
The Binary number system is used by most machines and electrical devices to communicate. It is also known as the base 2 number system, because each position in the number represents an incremental number with a base of 2. Since it is represented it 2s, there are only 2 numbers that can be a value in each position 0 or 1.
The CPU is the intelligence of the machine but it needs a pre-written program to create, use and modify the data. If the computer needs to compare two numbers, or add two numbers, this is carried out inside the CPU and the numbers have to be fetched into the CPU from the computer’s memory chip. The three main components of CPU are: Arithmetic logic Unit (ALU), Bus Interface unit, and the Control Bus.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) carries out all the calculations and decision making tasks. The ALU uses devices called gates that receive one or more inputs and based up what function they are designed to perform, outputs a result. The basic operations of an ALU include adding and subtracting binary values as well as performing logical operations such as AND, NOT, OR AND XOR.
The Bus Interface Unit takes the data to and from the CPU which is held inside internal registers (small memory stores) along the external Data Bus to read and write memory and devices. The Data Bus carries information in both directions. The Bus Interface Unit also places the required location addresses on the Address Bus, so that the required devices can be accessed for reading or writing.
The Control Bus is the physical connection that carries control information between the CPU and other devices within the computer. It decodes all program instructions and dictates all the CPU’s control and timing mechanisms. It sends out the read and write signals on the Control Bus.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход











 Basic Structure of Computer (41.88 KB)
Basic Structure of Computer (41.88 KB)
 0
0 355
355 0
0 Нравится
0
Нравится
0



