Today we are going to speak about conditional sentences of the second type.
Well, some of you probably think that this grammar rule is not so much important in everyday communication. However, we all like dreaming about something, don’t we?
Do you remember your dreams in childhood about being a pilot or a spaceman? Or even now when you are extremely tired after a hard day…

Don’t you think about going somewhere and having a perfect holiday?
So let’s see how to express grammatically correctly our wishes or desires which have no time limit.
In the English language the second type of conditional sentences is used in hypothetical, imaginary situations, they are unlikely to happen in the present or in the future. We can just imagine them in our mind or dream. Of course there is always a chance that our dream will come true, but it is just a fairy tale, in reality the percent is very low.
For example,
If I had a million dollars like Mr. Black, I would buy a luxurious car.
(But I am not so rich, that is why I use public transport.)
The formation of this conditional type is the following.
We have two parts in the sentence – the “if part” and the main part.

In the “if” part we have the subject and the predicate in the Past Simple Tense.
In the main part after the subject we use the Future Simple in the Past Tense (that is “would” plus the infinitive of a verb without the particle “to”). “Would” is often shortened to ‘d, especially in spoken English. As an illustration,
If our parents liked pets, we would have a dog or a cat.
(But our parents do not like pets).
If in the “if part” of the sentence we have the verb “TO BE”, it is used in the form “were” for all persons.

For example,
If he were older, he would go to the cinema to watch this horror film.
If she were not so strict, her pupils would not be afraid of her.
Besides, when we want to give a piece of advice we begin the sentence with “If I were you…” or “If I were in your position” or even spoken variant “If I were in your shoes…
For instance,
If I were in Jack’s position, I would not buy this mobile phone.
If I were in your shoes, I would not talk over the phone so much.
If I were you, I would not listen to Rammstein.
In the main part of the sentence after the subject instead of “would” we can also have modal verbs (could/should/might/ought to), but in such sentences the speaker is not so certain about the probability or the result.

Let’s compare,
If she knew the answer, she would tell me. (He is 100% sure about that.)
If she knew the answer, she might tell me. (It is possible to happen, but may be 50/50).
If he knew the answer, he should tell me. (It is very important for him, but he does not know how she would behave).
And now we are going to do some exercises.
In exercise 1 the task is to put the verbs into the correct form.
1. If I … (to have) an extra pencil, I would give it to you, but I do not have any. HAD
2. I would not mind living in Britain, if the weather … (not to be) so rainy. WERE NOT
3. If I were you, I … (not to spend) so much time playing computer games. WOULD NOT SPEND
4. She would help you, if she (to know) how.
KNEW
5. If you had longer legs, you (to be) an Olympic champion in athletics. WOULD BE
In exercise 2 the task is to comment on the situation using the second type of conditional sentences. For example,
He drinks 10 cups of coffee every day. As a result, he has problems with sleep.
If he did not drink 10 cups of coffee every day, he would not have problems with sleep.
1. His friends do not understand him because he speaks very fast.
2. If he did not speak very fast, his friends would understand him.
3. Paul is overweight because he likes fast food.
4. If Paul did not like fast food, he would not be overweight.
5. He can’t type very quickly, so she will not get this job.
6. If he typed (or we may say could type) quickly, he would get the job.
That is all for today! Now you can dream and imagine in English using the second type of conditionals.
Hope that you will express your dreams grammatically correctly and every wish in your dream bubble will come true!

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход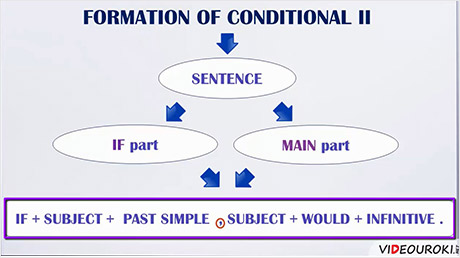


 0
0 989
989


