Hello, guys! Welcome to Grammar Zone! My name’s Harry Jones.
My best friends Allan and Kate will help me make our lessons useful and enjoyable.
Do you often wear T-shirts? – I’m sure you DO!
The T-shirt is one of the most popular items of clothing. Millions of them are sold every day all around the world. I’m pretty sure you own more than one (I, personally, own a lot more than one – I had 15 the last time I counted).
You might be wearing one just now. Actually, that’s the beauty of the T-shirt. It is worn by all kinds of different people, in many different countries.
However, things were not always like that. Up until the mid 20th century, T-shirts were made of 100% cotton and were worn only as underwear. In the 1950s white T-shirt became very popular with young people. They were cool and rebellious.
These days, T-shirts are made of different fibres, they come in all sizes, they are dyed in a great variety of colours and are decorated with text or pictures. They are even used to advertise products or to pass messages (e.g. “Save our planet –
Recycle”).

There are also shops where you can make your own T-shirt: you choose the size, colour and design and then you can print anything you like on them. The end product is as unique as you are!
Well, you might have known the underlined constructions. Are they active or passive? – Right you are, they are passive.
Today we are going to look at the Passive Voice.
By the end of this lesson you will have a good understanding of when to use the Passive voice and how to form the passive sentences.
So let’s get started.
A sentence generally begins with the person who does the action – subject (подлежащее), then goes the verb (сказуемое) and the object or person that the action is performed on (дополнение над которым совершено действие). This is called an “Active” sentence.
People wear T-shirts all around the world.

If we start the sentence with the object or person that the action is performed on, we form a “Passive” sentence.
The T-shirt is worn by all kinds of different people.
Millions of them are sold every day all around the world.
T-shirts are made of different fibres,
They are decorated with text or pictures.
We use the Passive:
· when the subject is unknown, unimportant or obvious (неизвестен, не важен или очевиден) from the context.
E.g.
The T-shirts are even used to advertise products or to pass messages. (We don’t know who uses them - unknown subject.)
All the tickets were sold out yesterday. (unimportant subject)
I haven’t been invited to Sam’s party. (by Sam - obvious subject)
· We also use the passive form when we are interested more in the action itself, not WHO performs it, such as in news reports, formal notices, instructions, processes, headlines, advertisements, etc.
E.g.
Feeding animals is not allowed. (written notice)
The local bank was robbed this morning. (news report)
Breakfast is served between 7-10.30 a.m. (formal notice)
· to make statements more formal or polite.
E.g. Passive: My car was broken. (more polite)
Active: You’ve broken my car. (less polite)
· to put emphasis on the subject.
E.g. The Lord Of The Rings was written by J. R. R. Tolkien.
Formation
We form the passive with the verb to be and the 3rd form of the main verb (past participle).
You have to be careful because the form of to be needs to be put in different tenses!
|
|
Active Voice |
Passive Voice |
|
Present Simple |
do/does |
am/is/are done |
|
Present Continuous |
am/is/are doing |
am/is/are being done |
|
Past Simple |
did |
was/were done |
|
Past Continuous |
was/were doing |
was/were being done |
|
Future Simple |
will do |
will be done |
|
Present Perfect |
have done |
have been done |
|
Past Perfect |
had done |
had been done |
|
Future Perfect |
will have done |
will have been done |
|
Infinitive |
to do |
to be done |
|
Modal Verbs |
must do |
must be done |
Changing from Active into Passive
When a sentence is turned from active into passive:
· the object of the active sentence becomes the subject in the passive sentence. (Дополнение в активном залоге становится подлежащим в пассивном залоге).
Remember that only verbs that take an object (transitive verbs – переходные глаголы) can become passive verbs:
E.g.
Active: His parents gave him some money.
Passive: Some money was given to him by his parents.
But: They slept well. (The verb sleep in this sentence is intransitive; not followed by an object. The sentence cannot be changed into the passive).
Some transitive verbs, such as have, fit, resemble, suit, seem, exist, etc. cannot be changed into the passive.
E.g.
I have got a dog.
These gloves fit me perfectly.
With verbs which take two objects such as bring, allow, award, buy, feed, give, hand, lend, offer, read, send, show, tell, write and etc., it is more usual to begin the passive sentence with the person.
We can make 2 different passive sentences.
Active: They offered Kate a job.

Passive: a) Kate was offered a job. (more usual)
b) A job was offered to Kate. (less usual)
The verbs make, see, help, and hear are followed by an infinitive without TO in the active, but by a to-infinitive in the passive.
Active: This song made me cry.
Passive: We were made to clean the bedroom.

BY or WITH?
In the passive sentences we can use by to say WHO or WHAT does the action (agent).
The bill was paid by Mr Carter.
The table will be covered by the waiter.
We can use with to talk about what instrument/material or ingredient is used to do the action.
The bill can be paid with the credit card.
The table will be covered with a white cloth.
In passive questions with who/whom/which we don’t omit BY.
Who was Australia discovered by?
What was the flood caused by?
What was the window broken with?
The agent is not omitted when it is a specific or an important person, or when it is essential to the meaning of the sentence.
E.g.
America was discovered by Columbus.
By + agent is omitted when the agent is unknown, unimportant, obvious from the context or referred to by words such as people, one, someone/somebody, they, he, etc.

Active: He fixed the car.
Passive: The car was fixed. (by him is omitted)
Now it’s time to practice the rule.
Complete the missing forms.
|
|
|
am/is/are done |
|
|
am/is/are doing |
|
|
Past Simple |
|
was/were done |
|
Past Continuous |
was/were doing |
|
|
Future Simple |
|
will be done |
|
|
|
have been done |
|
Past Perfect |
|
|
|
Future Perfect |
|
will have been done |
|
|
to do |
to be done |
|
Modal Verbs |
|
|
That`s all for today.
Join us at our grammar lessons at videouroki.net and you’ll be given a lot of useful information.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход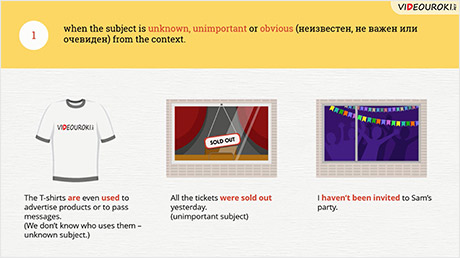



 1195
1195

