Hello, guys! I’m Tommy Wilson. Welcome to our grammar lessons!
My best friends Maddy, Kristie and Martin will help me make our lessons useful and enjoyable.
In the lesson today we’ll compare Past Simple and Present Perfect tenses:
- their formation and usage;
- time markers that help us to define them in the sentence,
and finally, we will practice the usage of these tenses in different situations.
So, first of all, let`s revise their formation.
We form the Past Simple with the help of the so called 2nd form of the verbs.
What two groups are all the verbs in the English language divided into?
Regular and Irregular.
To use a regular verb in the Past Simple tense, we just add –d or –ed to the main verb. Pay attention to the spelling rules!
E.g. open – opened
stop - stopped
carry – carried
stay – stayed
cycle - cycled
travel - travelled
To use an irregular verb in the Past Simple tense we use the list of irregular verbs.
E.g. take - took, see – saw, break - broke
And I can`t but mention, that you have to learn all the irregular verbs by heart!
E.g. He answered the phone.
They went to Spain last year.
We form the Present Perfect Tense with the help of auxiliary verb have for I/you/we/they and has when we use he/she/it in the sentence and the main verb in its 3rd form. We have already reminded you that regular verbs take –ed ending. We do the same to build their 3rd form. And irregular verbs can be found in the list of irregular verbs or learnt by heart).
E.g. They have been on a hot air balloon flight.
We all know, that to build negative and interrogative sentences in English we need at least two verbs: an auxiliary and a main one! (If we don`t have modal verbs or the verb ‘to be’).
To build negative and interrogative sentences in the Past Simple tense, we have to use the auxiliary verb ‘did’.
We form questions by putting Did before the subject.
E.g. Did he answer the phone?
We form negations with did not / didn’t.
E.g. He didn’t answer the phone.
Remember! In questions and negations, we take the base form of the verb.
In the Present Perfect the auxiliary verb is ‘have/has’. To build questions we put have/has before the subject.
E.g. Have they been on a hot air balloon flight?
And to build a negative sentence we use have not (haven’t) or has not (hasn’t).
E.g. They haven’t been on a hot air balloon flight.
We use both tenses the Past Simple and Present Perfect to talk about something that happened in the past. Let’s consider the difference in their meanings.
1.
· We use the Past Simple to talk about something that happened at a stated time in the past. We either say exactly or imply when it happened.
· We use the Present Perfect to put emphasis on the fact that something has happened. The exact time is either unknown or unimportant.
Compare the examples:

I bought a new laptop last week. (When did he buy it? Last week – stated time)

I have bought a new laptop. (When did he buy it? We don’t know. – unstated time).
2.
· We use the Past Simple to talk about the actions which started and finished in the past.
· We use the Present Perfect for actions and states that started in the past and continue up to the present.
Compare the examples:
Mrs Simpson taught English for thirty years.
(She is no longer a teacher. She has retired.)
Mrs Simpson has taught English for thirty years.

(She started teaching English thirty years ago and she is still teaching English today.)
3.
· We use the Past Simple to talk about the actions which happened in the past and cannot be repeated.
· We use the Present Perfect to talk about the actions which happened in the past and may be repeated.
Compare the examples:
Michael Schumacher won Formula One World Championship seven times. (He is no longer a racing driver. He cannot win another medal.)
Lewis Hamilton has won Formula One World Championship three times. (He is still a racing driver. He may win some more medals.)
4.
· We use the Past Simple for an actions which happened within a specific time period which is over at the moment of speaking.
· We use the Present Perfect for an action which happened within a specific time period which is not over at the moment of speaking.
Compare the examples:

She took a lot of photos yesterday. (The time period – yesterday – is over.)

She has taken a lot of photos today. (The time period – today – isn’t over. She may take some more photos.)
There are some other cases when we use these tenses. Let’s consider them either.
· The Past Simple is used for actions which happened one after the other.

E.g. She came in, introduced herself, and began to talk about her country.
· The Present Perfect is used to express actions which have finished so recently that there is evidence in the present.
E.g. I’ve just washed the dishes, fed the dog and cooked dinner. What about you, George?
I’ve just painted that bench. (The paint is wet.)
Don’t forget about the time markers that help us to define the tense.
Time expressions used with the Past Simple include:
yesterday
last night/week/month/year
two days/weeks/months ago
then
when
How long ago...?
in 2010
The Present Perfect is used with the following time markers:
already
yet (in negations and questions)
just
ever/never
so far
still (in negations)
lately/recently
today/this week/month/year, etc.
Choose the correct answer.
1. We have finished our homework. Can we go outside now?
(Present Perfect emphasizes the fact that homework has been finished. The exact time is unknown.)
2. She sealed the letter, put a stamp on it and posted it.
(The actions happened one after the other.)
3. Kate answered the phone when I called.
(The action happened at a stated period of time in the past – when I called)
4. Have you heard about John? He has broken his leg.
(Present Perfect emphasizes the fact that his leg has been broken. The exact time is unknown.)
5. I ate all the crisps last night, sorry!
(The action happened at a stated time in the past – last night)
6. I love this band. I have downloaded all their albums onto my MP3 player. (Present Perfect emphasizes the fact that he has downloaded all their albums. The exact time is unknown.)
7. Amy is so excited. She has just passed a driving test. (The action has finished so recently that there is evidence in the present – She is so excited.)
So now we can claim that now we know for sure:
· how to form the tenses correctly;
· in what situations to use these tenses;
· Don’t forget about the time markers that help us to define the tense correctly
Practice your grammar skills because practice makes PERFECT!

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход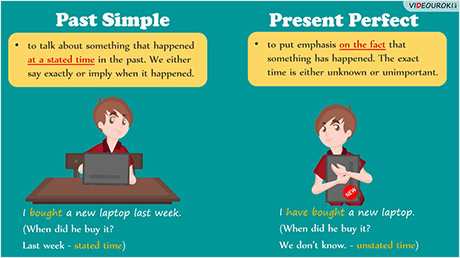


 0
0 2619
2619

