| Long term plan section: Programming solutions | School: CSI "Secondary school №13" akimat of the city of Rudny | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Date: | LF of the teacher: Anuchkina L.N. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: 7 | Number of missing: Number of attendees: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lesson topic | Programming of branching algorithms | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Learning objectives that are achieved in this lesson (link to the curriculum) | 7.3.2.1 - write the algorithm in a programming language 7.3.3.2 - write linear and branching algorithms in the integrated development environment of programs (C / C ++, Python, Delphi, Lazarus) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lesson objectives | know the concept of a branching algorithm, be able to write an algorithm in a programming language | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Success criteria | All students know the concept of branching. Most students can write branching algorithms in a programming language. Some students independently convert the template program in accordance with the proposed condition of the problem. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Languagegoals | Subject vocabulary and terminology: branching algorithm, program structure, variable description, data types, data input and output operators, assignment operator, branch operator (conditions), full form of conditional operator, incomplete form of conditional operator. A series of useful phrases for dialogue / writing: The branching algorithm is ... The condition (branch) operator is used for ... The main operators of the branching type program are ... | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Instilling values | Responsibility, cooperation, independence | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interdisciplinary communication | mathematics, logic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preliminary knowledge | linear algorithm, program structure, main program operators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
During the classes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scheduled lesson stages | Scheduled lesson activities | Resources | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The beginning of the lesson 1 min 3 min
6 min
| Organizing moment: Greetings, checking those present. Creating a positive emotional background. Set the working mood. We continue to learn programming algorithms. We will begin the lesson with the words of Maciej Kaczmarek, a Polish programmer. Программирование – это когда идеи воплощаются в реальные вещи. - How do you understand these words? … Homework check: We programmed linear type algorithms in the last lesson. Call to memory the basic concepts on this topic. - What is called a linear algorithm? … Task «Set match» /Frontal work/. Match the keywords, operators, and data types used in Pascal with their meaning.
Task “Programming of linear algorithm” (formative estimation). - Read the evaluation criteria. - What should you know and be able to? … Evaluation Criteria: - knows the concept of a linear algorithm, - can write linear algorithms in a programming language, - independently transforms the template program in accordance with the proposed task condition. Completing of the work. Conclusion / Mutual testing | Presentation Presentation, individual cards Programming of linear algorithm (cards of FE) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
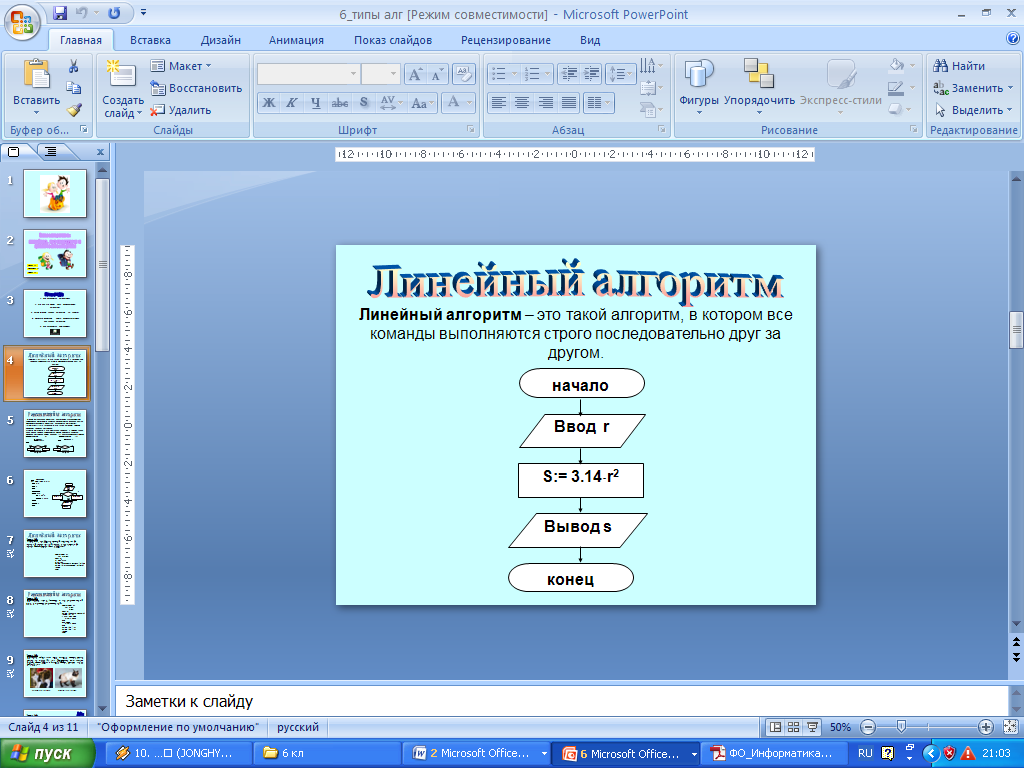
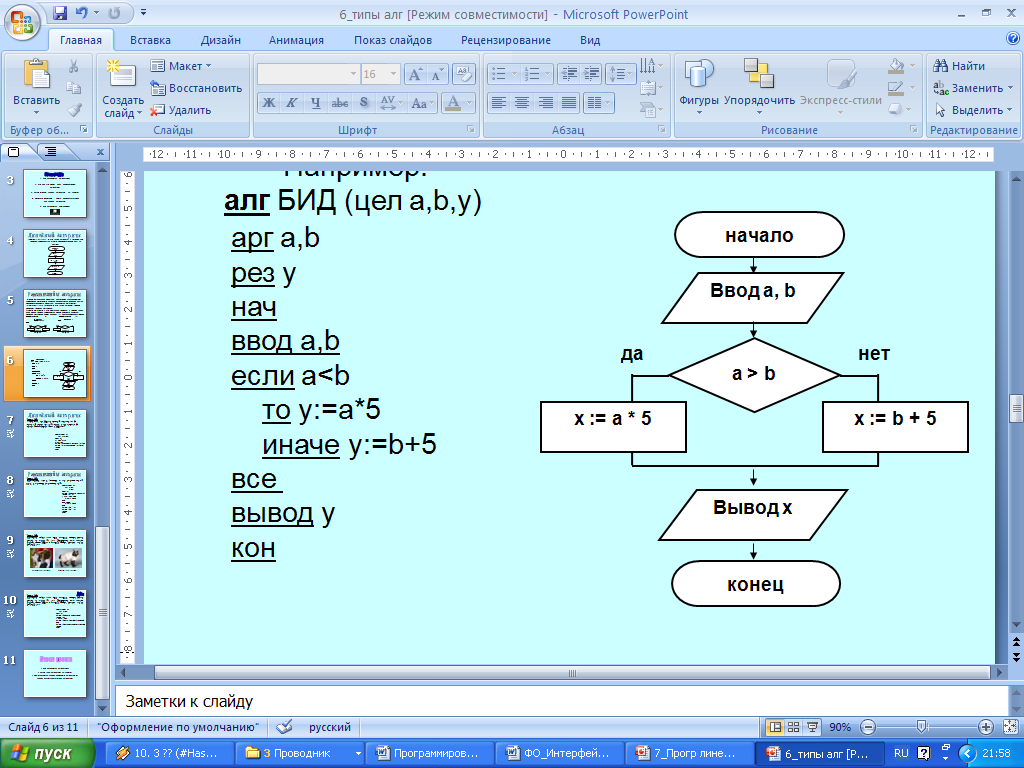
| Middle of the lesson 25 min | Update of supporting knowledge: We learned to program a linear algorithm in the last lesson. - What is a linear algorithm? Look at the 2nd illustration and say: - What is the peculiarity of this algorithm? - How can you call this type of algorithm? … - Name the topic of our lesson today. … - Identify the goals of our work in class today. … - Read the success criteria for your work. Success criteria: - knows the concept of branching algorithm, - can write branching algorithms in a programming language - independently transforms the template program in accordance with the proposed task condition. Explanation of a new topic: Now let's move on to learning a new topic. We will have 4 groups today. Questions to study of 1 group: 1. The concept of the branching algorithm. 2. Examples of tasks containing the branching algorithm. Questions to study of 2 group: Conditional statement: a) the general form of the record, b) logical expressions. Questions to study of 3 group: Forms of branching: a) the full form of branching, b) incomplete form of branching. Questions to study of 4 group: The structure of the program branching type. We study the topic in the group. Then 1 speaker of each group moves to another group and shares knowledge with the members of the new group. Method "Carousel" Conclusion. Primary consolidation: "Chamomile of Bloom" /Frontal work/ - Что называется алгоритмом ветвления? - Если правильно понимать, то в алгоритме ветвления действия не могут идти строго последовательно друг за другом? - Почему алгоритм «Светофор» является алгоритмом ветвления? - Что будет, если переставить местами команды алгоритма с ветвлением? - Как можно сделать из линейного алгоритма «Приготовление бутерброда» алгоритм с ветвлением? - Чем алгоритм ветвления отличается от линейного алгоритма? Task “Programming of branching algorithms” (formative estimation). Evaluation Criteria: - knows the concept of branching algorithm, - can write branching algorithms in a programming language - independently transforms the template program in accordance with the proposed task condition. Self test | Presentation Presentation Presentation Programming of branching algorithms (cards of FE), Pascal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| End of the lesson 5 min
| Reflection of activities in the classroom: I know ... / I can ... / Independently ... Achieve your own goals. We have 3 levels: "Knowledge", "Skill" and "Independent work". Determine which level you climbed today. - Who completed the task №1 without errors? - What were the difficulties in performing this task? … You are at level 1. - Who completed the task №2 without errors? - What were the difficulties in performing this task? … You are at level 2. - Who completed the task №3 without errors? - What were the difficulties in performing this task? ... You are at level 3. Summing up the lesson: - Какой алгоритм называется алгоритмом ветвления? - Какие существуют формы записи алгоритмов ветвления? - Как записывается условный оператор в полной форме?
Homework: To study the abstract material, to teach the program operators. | Presentation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Material for checking homework, explaining the new topic and checking the mastery of the material is used in Russian.

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход












 Урок информатики по теме "Программирование алгоритмов ветвления" (7 класс, двуязычие, ОСО) (337.3 KB)
Урок информатики по теме "Программирование алгоритмов ветвления" (7 класс, двуязычие, ОСО) (337.3 KB)
 0
0 270
270 5
5 Нравится
0
Нравится
0


