1. Learn new vocabulary
| carrier-based | aeroplane | базирующийся на авианосец самолёт |
|
| aircraft | самолет, летательный аппарат, воздушное судно |
| heavier-than-air | aircraft | летательный аппарат тяжёлее воздуха |
| lighter-than-air | aircraft | летательный аппарат лёгче воздуха |
| ultra-light | aircraft | сверхлегкий летательный аппарат |
| vertical takeoff and landing | aircraft | самолёт вертикального взлёта и посадки |
| short takeoff and landing | aircraft | самолёт короткого взлёта и посадки |
| paved runway | aircraft | ВПП с твёрдым покрытием |
| commercial | aircraft | пассажирский самолет |
| cargo | aircraft | грузовое воздушное судно |
| freight | aircraft | грузовое воздушное судно |
| local service | aircraft | самолет местных авиалиний |
| jet | airliner | реактивный авиалайнер |
|
| airplane | самолет, летательный аппарат, воздушное судно |
|
| airship | дирижабль |
|
| amphibian | самолет-амфибия |
|
| balloon | воздушный шар, аэростат |
|
| craft | самолет, летательный аппарат, воздушное судно |
| basic | dimensions | основные размеры |
|
| empennage | оперение |
| leading edge | flaps | щитки передней кромки |
| trailing edge | flaps | закрылки |
Airplane is an engine-driven vehicle that can fly through the air supported by the action of air against its wings. Airplanes are heavier than air, in contrast to vehicles such as balloons and airships, which are lighter than air. Airplanes also differ from other heavier- than-air craft, such as helicopters, because they have rigid wings; control surfaces, movable parts of the wings and tail, which make it possible to guide their flight; and power plants, or special engines that permit level or climbing flight.
Modern airplanes range from ultra light aircraft weighing no more than 46 kg (100 lb) and meant to carry a single pilot, to great jumbo jets, capable of carrying several hundred people, several hundred tons of cargo, and weighing nearly 454 metric tons.
Airplanes are adapted to specialized uses. Today there are land planes (aircraft that take off from and land on the ground), seaplanes (aircraft that take off from and land on water), amphibians (aircraft that can operate on both land and sea), and some airplanes that can leave the ground using the jet thrust of their engines or rotors (rotating wings) and then switch to wing-borne flight.
Types of airplanesThere are a wide variety of types of airplanes. Land planes, carrier-based airplanes, seaplanes, amphibians, vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL), short takeoff and landing (STOL), and space shuttles all take advantage of the same basic technology, but their capabilities and uses make them seem only distantly related.
Land planes are designed to operate from a hard surface, typically a paved runway. Some land planes are specially equipped to operate from grass or other unfinished surfaces. A land plane usually has wheels to taxi, take off, and land, though some specialized aircraft operating in the Arctic or Antarctic regions have skis in place of wheels. The wheels are sometimes referred to as the undercarriage, although they are often called, together with the associated brakes, the landing gear. Landing gear may be fixed, as in some general-aviation airplanes, or retractable, usually into the fuselage or wings, as in more-sophisticated airplanes in general and commercial aviation.
Classes of airplanesAirplanes can be grouped into a handful of major classes, such as commercial, military, and general-aviation airplanes, all of which fall under different certification and operating rules.
Commercial Airplanes. Commercial aircraft are those used for profit making, usually by carrying cargo or passengers for hire. They are strictly regulated—in the United States, by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA); and in other countries, by other national aviation authorities. Modern large commercial-airplane manufacturers—such as Boeing and McDonnell Douglas, which announced their merger in 1996, and Airbus Industries, a consortium of European manufacturers from Britain, Germany, France, and Spain—offer a wide variety of aircraft with different capabilities. Today’s jet airliners carry anywhere from 100 passengers to nearly 600 over short distances and over great lengths.
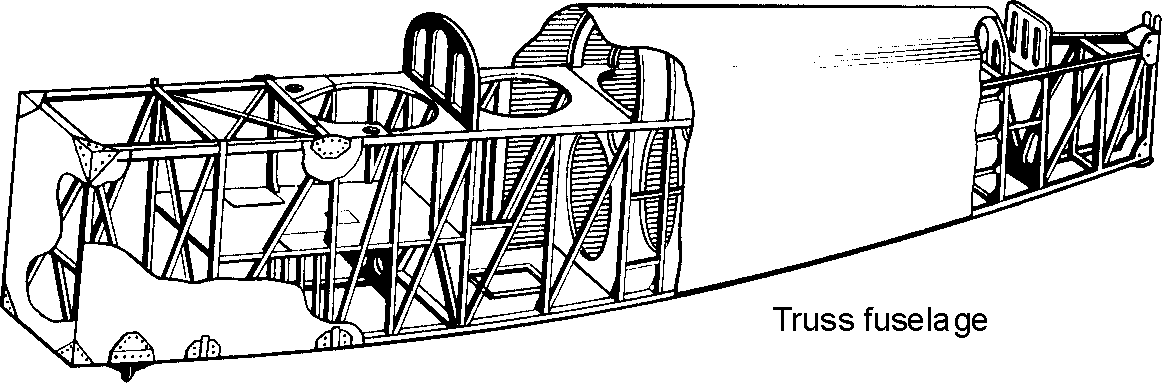
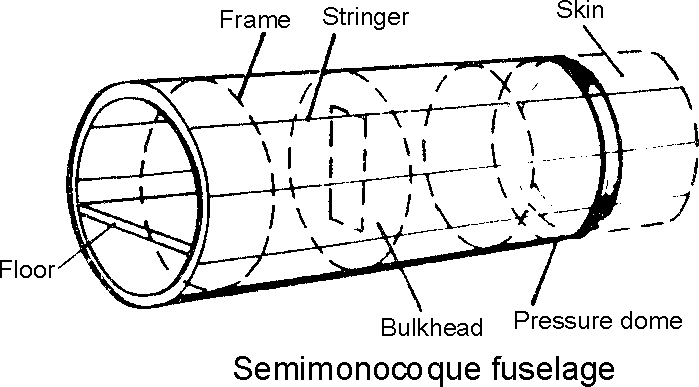
Modern airplanes have a semi-monocoque fuselage, a full cantilever wing, with a nose gear and two main landing gears. The empennage consists of the aft fuselage, vertical stabilizer, and the horizontal stabilizer. An auxiliary power unit (APU) is mounted in the empennage.
Trailing edge flaps and leading edge flaps and slats are used to reduce the takeoff and landing speeds. On the upper side of the wing spoiler panels may be raised to destroy lift.
Each engine is housed in a nacelle attached by a pylon (strut) to the underside of the wing.
According to Fuselage configuration
|
Classic configuration aircraft (single fuselage) |
|
|
Twin-fuselage a/c |
|
|
Twin-boom fuselage a/c |
|
According to number of wings
| Monoplane (моноплан) |
|
| Biplane (биплан) |
|
| Sesquiplane (полутораплан) |
|
| Triplane (триплан) | Three wings |
| Polyplane (полиплан) | Four and more wings |
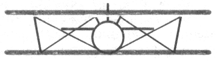
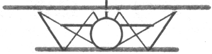
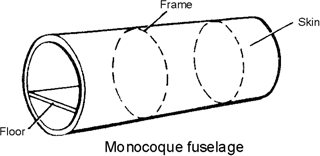
According to Fuselage structure
|
F u s e l a g e |
Truss-type fuselage | | |
| (ферменный) | |||
|
|
Monocoque | | |
|
| (балочно-обшивочный, | ||
|
| монококовый | ||
|
| или монокок) | ||
| Beam-type fuselage |
| ||
| (балочный) |
| ||
|
| | ||
|
| Semimonocoque | ||
|
| (балочно-стрингерный, | ||
|
| полумонококовый | ||
|
| или полумонокок) | ||
Wings with respect to body
|
High-wing (monoplane) (высокоплан) |
|
| Midwing (monoplane) (среднеплан) |
|
|
Low-wing (monoplane) (низкоплан) |
|

 Получите свидетельство
Получите свидетельство Вход
Вход












 Методическая разработка: "Types of airplanes" (152 KB)
Методическая разработка: "Types of airplanes" (152 KB)
 0
0 97
97 1
1 Нравится
0
Нравится
0


